Downregulation of Mcl-1 through GSK-3β activation contributes to arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells
- PMID: 22751450
- PMCID: PMC3478411
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2012.180
Downregulation of Mcl-1 through GSK-3β activation contributes to arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells
Abstract
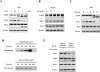
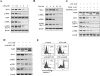
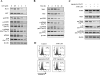
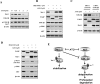
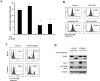
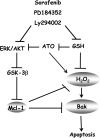
Arsenic trioxide (ATO) induces disease remission in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) patients, but not in non-APL acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. ATO at therapeutic concentrations (1-2 μM) induces APL NB4, but not non-APL HL-60, cells to undergo apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. The role of antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1 in ATO-induced apoptosis was determined. The levels of Mcl-1 were decreased in NB4, but not in HL-60, cells after ATO treatment through proteasomal degradation. Both glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) inhibitor SB216763 and siRNA blocked ATO-induced Mcl-1 reduction as well as attenuated ATO-induced apoptosis in NB4 cells. Silencing Mcl-1 sensitized HL-60 cells to ATO-induced apoptosis. Both ERK and AKT inhibitors decreased Mcl-1 levels and enhanced ATO-induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Sorafenib, an Raf inhibitor, activated GSK-3β by inhibiting its phosphorylation, decreased Mcl-1 levels and decreased intracellular glutathione levels in HL-60 cells. Sorafenib plus ATO augmented reactive oxygen species production and apoptosis induction in HL-60 cells and in primary AML cells. These results indicate that ATO induces Mcl-1 degradation through activation of GSK-3β in APL cells and provide a rationale for utilizing ATO in combination with sorafenib for the treatment of non-APL AML patients.
Figures

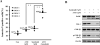
References
-
- Park JH, Tallman MS. Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia without cytotoxic chemotherapy. Oncology (Williston Park) 2011;25:733–741. - PubMed
-
- Soignet SL, Maslak P, Wang ZG, Jhanwar S, Calleja E, Dardashti LJ, et al. Complete remission after treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1341–1348. - PubMed
-
- Jing Y, Wang L, Xia L, Chen GQ, Chen Z, Miller WH, et al. Combined effect of all-trans retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 2001;97:264–269. - PubMed
-
- Chen GQ, Shi XG, Tang W, Xiong SM, Zhu J, Cai X, et al. Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): I. As2O3 exerts dose-dependent dual effects on APL cells. Blood. 1997;89:3345–3353. - PubMed
-
- Dai J, Weinberg RS, Waxman S, Jing Y. Malignant cells can be sensitized to undergo growth inhibition and apoptosis by arsenic trioxide through modulation of the glutathione redox system. Blood. 1999;93:268–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

