The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor and stem cell biology
- PMID: 22751497
- PMCID: PMC3403009
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.193730.112
The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor and stem cell biology
Abstract
Stem cells play a critical role during embryonic development and in the maintenance of homeostasis in adult individuals. A better understanding of stem cell biology, including embryonic and adult stem cells, will allow the scientific community to better comprehend a number of pathologies and possibly design novel approaches to treat patients with a variety of diseases. The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor RB controls the proliferation, differentiation, and survival of cells, and accumulating evidence points to a central role for RB activity in the biology of stem and progenitor cells. In some contexts, loss of RB function in stem or progenitor cells is a key event in the initiation of cancer and determines the subtype of cancer arising from these pluripotent cells by altering their fate. In other cases, RB inactivation is often not sufficient to initiate cancer but may still lead to some stem cell expansion, raising the possibility that strategies aimed at transiently inactivating RB might provide a novel way to expand functional stem cell populations. Future experiments dedicated to better understanding how RB and the RB pathway control a stem cell's decisions to divide, self-renew, or give rise to differentiated progeny may eventually increase our capacity to control these decisions to enhance regeneration or help prevent cancer development.
Figures
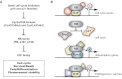
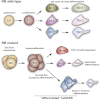
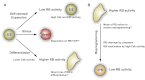
References
-
- Barta T, Vinarsky V, Holubcova Z, Dolezalova D, Verner J, Pospisilova S, Dvorak P, Hampl A 2010. Human embryonic stem cells are capable of executing G1/S checkpoint activation. Stem Cells 28: 1143–1152 - PubMed
-
- Becker KA, Ghule PN, Therrien JA, Lian JB, Stein JL, van Wijnen AJ, Stein GS 2006. Self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells is supported by a shortened G1 cell cycle phase. J Cell Physiol 209: 883–893 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
