In vitro synergy of colistin combinations against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates
- PMID: 22751540
- PMCID: PMC3421898
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.05996-11
In vitro synergy of colistin combinations against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates
Abstract
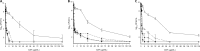
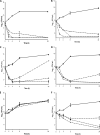
Colistin resistance, although uncommon, is increasingly being reported among Gram-negative clinical pathogens, and an understanding of its impact on the activity of antimicrobials is now evolving. We evaluated the potential for synergy of colistin plus trimethoprim, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (1/19 ratio), or vancomycin against 12 isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii (n = 4), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (n = 4), and Klebsiella pneumoniae (n = 4). The strains included six multidrug-resistant clinical isolates, K. pneumoniae ATCC 700603, A. baumannii ATCC 19606, P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853, and their colistin-resistant derivatives (KPm1, ABm1, and PAm1, respectively). Antimicrobial susceptibilities were assessed by broth microdilution and population analysis profiles. The potential for synergy of colistin combinations was evaluated using a checkerboard assay, as well as static time-kill experiments at 0.5× and 0.25× MIC. The MIC ranges of vancomycin, trimethoprim, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (1/19) were ≥128, 4 to ≥128, and 2/38 to >128/2,432 μg/ml, respectively. Colistin resistance demonstrated little impact on vancomycin, trimethoprim, or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole MIC values. Isolates with subpopulations heterogeneously resistant to colistin were observed to various degrees in all tested isolates. In time-kill assays, all tested combinations were synergistic against KPm1 at 0.25× MIC and 0.5× MIC and ABm1 and PAm1 at 0.5× MIC. In contrast, none of the tested combinations demonstrated synergy against any colistin-susceptible P. aeruginosa isolates and clinical strains of K. pneumoniae isolates. Only colistin plus trimethoprim or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole was synergistic and bactericidal at 0.5× MIC against K. pneumoniae ATCC 700603. Colistin resistance seems to promote the in vitro activity of unconventional colistin combinations. Additional experiments are warranted to understand the clinical significance of these observations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro activity of the siderophore monosulfactam BAL30072 against contemporary Gram-negative pathogens from New York City, including multidrug-resistant isolates.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014 Jun;43(6):527-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.02.017. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014. PMID: 24796217
-
In Vitro Synergistic Activity of Antimicrobial Agents in Combination against Clinical Isolates of Colistin-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Oct 21;60(11):6774-6779. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00839-16. Print 2016 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27600048 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro time-kill studies of antimicrobial agents against blood isolates of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, including colistin- or tigecycline-resistant isolates.J Med Microbiol. 2012 Mar;61(Pt 3):353-360. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.036939-0. Epub 2011 Oct 20. J Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22016557
-
Synergistic combinations of polymyxins.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016 Dec;48(6):607-613. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.09.014. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016. PMID: 27865626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymyxins: Antimicrobial susceptibility concerns and therapeutic options.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2011 Jul-Sep;29(3):230-42. doi: 10.4103/0255-0857.83905. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21860102 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical experience of colistin-glycopeptide combination in critically ill patients infected with Gram-negative bacteria.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(2):851-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00871-13. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24277037 Free PMC article.
-
Ca-EDTA restores the activity of ceftazidime-avibactam or aztreonam against carbapenemase-producing Klebsiellapneumoniae infections.iScience. 2023 Jun 28;26(7):107215. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107215. eCollection 2023 Jul 21. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37496674 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Bactericidal Activity of Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole Alone and in Combination with Colistin against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Oct 21;60(11):6903-6906. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01082-16. Print 2016 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27550356 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-microbial, anti-biofilm activities and cell selectivity of the NRC-16 peptide derived from witch flounder, Glyptocephalus cynoglossus.Mar Drugs. 2013 May 28;11(6):1836-52. doi: 10.3390/md11061836. Mar Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23760014 Free PMC article.
-
Novel nitroxoline derivative combating resistant bacterial infections through outer membrane disruption and competitive NDM-1 inhibition.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024 Dec;13(1):2294854. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2294854. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 38085067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antoniadou A, et al. 2007. Colistin-resistant isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae emerging in intensive care unit patients: first report of a multiclonal cluster. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 59:786–790 - PubMed
-
- Bercot B, Poirel L, Dortet L, Nordmann P. 2011. In vitro evaluation of antibiotic synergy for NDM-1-producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 66:2295–2297 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

