Metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriatic disease
- PMID: 22751586
- PMCID: PMC3670770
- DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.120237
Metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriatic disease
Abstract
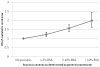
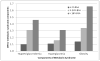
Psoriasis is a common Th-1 and Th-17-mediated chronic inflammatory disease that has been associated with metabolic syndrome, a constellation of cardiovascular risk factors including obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance. Overlapping inflammatory pathways and genetic susceptibility may be potential biologic links underlying this association. Multiple epidemiologic studies have consistently demonstrated higher prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriasis. Dose-response relationships between more severe psoriasis and higher prevalence of metabolic syndrome components were recently established. This association has important clinical implications for the comprehensive management of psoriasis: Patients with psoriasis should be routinely screened for metabolic syndrome and treated accordingly to manage cardiometabolic risk, while clinicians should monitor potential effects on treatment efficacy and safety in patients with comorbid psoriasis and metabolic syndrome. Further research will be necessary to establish the directionality of this association and to explore the effect of treatment on these comorbid diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Gelfand JM, Neimann AL, Shin DB, Wang X, Margolis DJ, Troxel AB. Risk of myocardial infarction in patients with psoriasis. JAMA. 2006 Oct 11;296(14):1735–41. - PubMed
-
- Gelfand JM, Feldman SR, Stern RS, Thomas J, Rolstad T, Margolis DJ. Determinants of quality of life in patients with psoriasis: a study from the US population. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004 Nov;51(5):704–8. - PubMed
-
- Gelfand JM, Troxel AB, Lewis JD, Kurd SK, Shin DB, Wang X, et al. The risk of mortality in patients with psoriasis: results from a population-based study. Arch Dermatol. 2007 Dec;143(12):1493–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
