Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency promotes the alternative activation of adipose tissue macrophages
- PMID: 22751700
- PMCID: PMC3478520
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-1595
Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency promotes the alternative activation of adipose tissue macrophages
Abstract
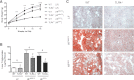
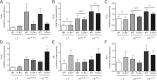
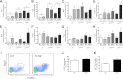
Obesity is characterized by adipose tissue (AT) macrophage (ATM) accumulation, which promotes AT inflammation and dysfunction. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) deficiency attenuates AT inflammation in obesity but does not impede the accumulation of ATMs. The purpose of the current study was to determine whether TLR4 deficiency alters ATM polarization. TLR4(-/-) and wild-type mice were fed a low-fat, high-monounsaturated fat (HF(MUFA)), or a high-saturated fat (HF(SFA)) diet for 16 weeks. Further, we used a bone marrow transplant model to determine the influence of hematopoietic cell TLR4 signaling. The metabolic and inflammatory responses to high-fat feeding and ATM phenotype were assessed. Global and hematopoietic cell TLR4 deficiency, irrespective of recipient genotype, produced a shift in ATM phenotype toward an alternatively activated state, which was accompanied by reduced AT inflammation. Despite the observed shift in ATM phenotype, neither global nor hematopoietic cell TLR4 deficiency influenced systemic insulin sensitivity after high-fat feeding. Results of the current study suggest that TLR4 directly influences ATM polarization but question the relevance of TLR4 signaling to systemic glucose homeostasis in obesity.
Figures




References
-
- Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993;259:87–91 - PubMed
-
- Gregor MF, Hotamisligil GS. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu Rev Immunol 2011;29:415–445 - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA., Jr A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature 1997;388:394–397 - PubMed
-
- Lee JY, Sohn KH, Rhee SH, Hwang D. Saturated fatty acids, but not unsaturated fatty acids, induce the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 mediated through Toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem 2001;276:16683–16689 - PubMed
-
- Radin MS, Sinha S, Bhatt BA, Dedousis N, O’Doherty RM. Inhibition or deletion of the lipopolysaccharide receptor Toll-like receptor-4 confers partial protection against lipid-induced insulin resistance in rodent skeletal muscle. Diabetologia 2008;51:336–346 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK-07563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089466/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090262/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK091040/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL-089466/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK-058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-091040/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK054902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-59637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

