Risk estimation and risk prediction using machine-learning methods
- PMID: 22752090
- PMCID: PMC3432206
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-012-1194-y
Risk estimation and risk prediction using machine-learning methods
Abstract
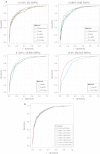
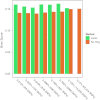
After an association between genetic variants and a phenotype has been established, further study goals comprise the classification of patients according to disease risk or the estimation of disease probability. To accomplish this, different statistical methods are required, and specifically machine-learning approaches may offer advantages over classical techniques. In this paper, we describe methods for the construction and evaluation of classification and probability estimation rules. We review the use of machine-learning approaches in this context and explain some of the machine-learning algorithms in detail. Finally, we illustrate the methodology through application to a genome-wide association analysis on rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson J. Separate sample logistic discrimination. Biometrika. 1972;59:19–35. doi: 10.1093/biomet/59.1.19. - DOI
-
- Arminger G, Enache D. Statistical models and artificial neural networks. In: Bock H, Polasek W, editors. Data analysis and information systems. Heidelberg: Springer; 1996. pp. 243–260.
-
- Arshadi N, Chang B, Kustra R. Predictive modeling in case–control single-nucleotide polymorphism studies in the presence of population stratification: a case study using Genetic Analysis Workshop 16 Problem 1 dataset. BMC Proc. 2009;3(Suppl 7):S60. doi: 10.1186/1753-6561-3-s7-s60. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banerjee M, Ding Y, Noone A (2012) Identifying representative trees from ensembles. Stat Med 31:1601–1616. doi:10.1002/sim.4492 4 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

