Serratia marcescens quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase activity mediates medium acidification and inhibition of prodigiosin production by glucose
- PMID: 22752173
- PMCID: PMC3416624
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01778-12
Serratia marcescens quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase activity mediates medium acidification and inhibition of prodigiosin production by glucose
Abstract
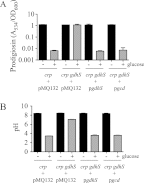
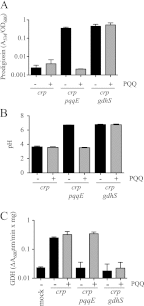
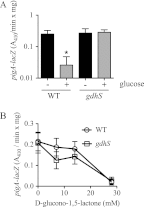
Serratia marcescens is a model organism for the study of secondary metabolites. The biologically active pigment prodigiosin (2-methyl-3-pentyl-6-methoxyprodiginine), like many other secondary metabolites, is inhibited by growth in glucose-rich medium. Whereas previous studies indicated that this inhibitory effect was pH dependent and did not require cyclic AMP (cAMP), there is no information on the genes involved in mediating this phenomenon. Here we used transposon mutagenesis to identify genes involved in the inhibition of prodigiosin by glucose. Multiple genetic loci involved in quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) activity were found to be required for glucose inhibition of prodigiosin production, including pyrroloquinoline quinone and ubiquinone biosynthetic genes. Upon assessing whether the enzymatic products of GDH activity were involved in the inhibitory effect, we observed that d-glucono-1,5-lactone and d-gluconic acid, but not d-gluconate, were able to inhibit prodigiosin production. These data support a model in which the oxidation of d-glucose by quinoprotein GDH initiates a reduction in pH that inhibits prodigiosin production through transcriptional control of the prodigiosin biosynthetic operon, providing new insight into the genetic pathways that control prodigiosin production. Strains generated in this report may be useful in large-scale production of secondary metabolites.
Figures



References
-
- Anthony C. 2004. The quinoprotein dehydrogenases for methanol and glucose. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 428: 2–9 - PubMed
-
- Ben Farhat M, et al. 2009. Characterization of the mineral phosphate solubilizing activity of Serratia marcescens CTM 50650 isolated from the phosphate mine of Gafsa. Arch. Microbiol. 191: 815–824 - PubMed
-
- Bouvet OM, Grimont PA. 1988. Extracellular oxidation of d-glucose by some members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Ann. Inst. Pasteur Microbiol. 139: 59–77 - PubMed
-
- Bunting MI, Robinow CF, Bunting H. 1949. Factors affecting the elaboration of pigment and polysaccharide by Serratia marcescens. J. Bacteriol. 58: 114 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

