Keap1-nrf2 signaling: a target for cancer prevention by sulforaphane
- PMID: 22752583
- PMCID: PMC3553557
- DOI: 10.1007/128_2012_339
Keap1-nrf2 signaling: a target for cancer prevention by sulforaphane
Abstract
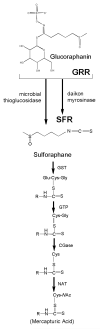
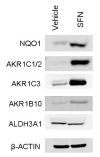
Sulforaphane is a promising agent under preclinical evaluation in many models of disease prevention. This bioactive phytochemical affects many molecular targets in cellular and animal models; however, amongst the most sensitive is Keap1, a key sensor for the adaptive stress response system regulated through the transcription factor Nrf2. Keap1 is a sulfhydryl-rich protein that represses Nrf2 signaling by facilitating the polyubiquitination of Nrf2, thereby enabling its subsequent proteasomal degradation. Interaction of sulforaphane with Keap1 disrupts this function and allows for nuclear accumulation of Nrf2 and activation of its transcriptional program. Enhanced transcription of Nrf2 target genes provokes a strong cytoprotective response that enhances resistance to carcinogenesis and other diseases mediated by exposures to electrophiles and oxidants. Clinical evaluation of sulforaphane has been largely conducted by utilizing preparations of broccoli or broccoli sprouts rich in either sulforaphane or its precursor form in plants, a stable β-thioglucose conjugate termed glucoraphanin. We have conducted a series of clinical trials in Qidong, China, a region where exposures to food- and air-borne carcinogens has been considerable, to evaluate the suitability of broccoli sprout beverages, rich in either glucoraphanin or sulforaphane or both, for their bioavailability, tolerability, and pharmacodynamic action in population-based interventions. Results from these clinical trials indicate that interventions with well characterized preparations of broccoli sprouts may enhance the detoxication of aflatoxins and air-borne toxins, which may in turn attenuate their associated health risks, including cancer, in exposed individuals.
Figures
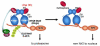
Similar articles
-
Regulation of the Keap1/Nrf2 system by chemopreventive sulforaphane: implications of posttranslational modifications.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Jul;1229:184-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06092.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011. PMID: 21793854 Review.
-
Identification of sensor cysteines in human Keap1 modified by the cancer chemopreventive agent sulforaphane.Chem Res Toxicol. 2005 Dec;18(12):1917-26. doi: 10.1021/tx0502138. Chem Res Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 16359182
-
Targeting NRF2 signaling for cancer chemoprevention.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010 Apr 1;244(1):66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.08.028. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19732782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of chemical activation of Nrf2.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035122. Epub 2012 Apr 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558124 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant sulforaphane and sensitizer trinitrobenzene sulfonate induce carboxylesterase-1 through a novel element transactivated by nuclear factor-E2 related factor-2.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Sep 15;84(6):864-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.06.025. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22776248 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevention of Carcinogen-Induced Oral Cancer by Sulforaphane.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2016 Jul;9(7):547-57. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-15-0290. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2016. PMID: 27339168 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Endotoxemia with Dietary Factors.Nutrients. 2019 Sep 23;11(10):2277. doi: 10.3390/nu11102277. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31547555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrophysiological, Morphologic, and Transcriptomic Profiling of the Ogura-CMS, DGMS and Maintainer Broccoli Lines.Plants (Basel). 2022 Feb 21;11(4):561. doi: 10.3390/plants11040561. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214894 Free PMC article.
-
A Bibliometric Review of the Keap1/Nrf2 Pathway and its Related Antioxidant Compounds.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Sep 1;8(9):353. doi: 10.3390/antiox8090353. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31480567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large insertion in radish GRS1 enhances glucoraphanin content in intergeneric hybrids, Raphanobrassica (Raphanus sativus L. x Brassica oleracea var. acephala).Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jun 6;14:1132302. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1132302. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37346118 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

