An excellent delivery system for improving the oral bioavailability of natural vitamin E in rats
- PMID: 22752681
- PMCID: PMC3429676
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-012-9819-y
An excellent delivery system for improving the oral bioavailability of natural vitamin E in rats
Abstract
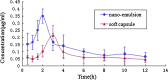
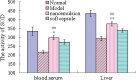
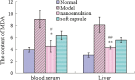
This study set out to develop a novel and stable nanoemulsion formulation of natural vitamin E with increased oral bioavailability. The natural vitamin E nanoemulsion was prepared by a modified emulsification technique. The physicochemical characteristics of natural vitamin E nanoemulsion were characterized and its pharmacokinetics study was performed as well. The experimental results showed droplet diameters ranging from 20 to 400 nm (average, 87.7 nm) with a negative electrostatic potential (-23.5 ± 1.5 mv). The pharmacokinetics study of this nanoemulsion and corresponding soft capsule was carried out using noncompartment model method. Compared with the marketed soft capsule, the C (max) of the natural vitamin E nanoemulsion was higher, while the T (max) was shorter. Thus, plasma concentration-time profiles in rats dosed with nanoemulsion showed a 1.6-fold enhancement in the area under the curve of natural vitamin E compared with the marketed soft capsule. The antioxidative effects of the natural vitamin E nanoemulsion and the marketed soft capsule were also evaluated by the levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration in serum and liver tissue. According to the SOD activity and the MDA concentration determined, the nanoemulsion was superior to the marketed soft as an antioxidative agent. The overall results demonstrated that the nanoemulsion drug delivery system could be a promising strategy for the delivery of natural vitamin E, which showed great potential for clinical application.
Figures

References
-
- Bjorneboe A, Bjorneboe GE, Drevon CA. Absorption, transport and distribution of vitamin E. J Nutr. 1990;3:233–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

