Treatment of first recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection: fidaxomicin versus vancomycin
- PMID: 22752865
- PMCID: PMC3388030
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cis462
Treatment of first recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection: fidaxomicin versus vancomycin
Abstract
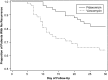
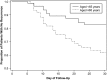
Recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) occurs in approximately 25% of successfully treated patients. Two phase 3 randomized, double-blind trials were conducted at 154 sites in the United States, Canada, and Europe to compare fidaxomicin vs vancomycin in treating CDI. Patients with CDI received fidaxomicin 200 mg twice daily or vancomycin 125 mg 4 times daily for 10 days. The primary end point was clinical cure of CDI at end of treatment, and a secondary end point was recurrence during the 28 days following clinical cure. In all, 1164 subjects were enrolled, of which a subgroup of 128 in the per-protocol population had another recent episode of CDI prior to the CDI diagnosis at study enrollment. In the analysis of this subgroup, initial response to therapy was similar for both drugs (>90% cure). However, recurrence within 28 days occurred in 35.5% of patients treated with vancomycin and 19.7% of patients treated with fidaxomicin (-15.8% difference; 95% confidence interval, -30.4% to -0.3%; P = .045). Early recurrence (within 14 days) was reported in 27% of patients treated with vancomycin and 8% of patients treated with fidaxomicin (P = .003). In patients with a first recurrence of CDI, fidaxomicin was similar to vancomycin in achieving a clinical response at end of therapy but superior in preventing a second recurrence within 28 days.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00314951 NCT00468728.
Figures
References
-
- Johnson S. Recurrent Clostridium difficile infection: a review of risk factors, treatments, and outcomes. J Infect. 2009;58:403–10. - PubMed
-
- Baines SD, O'Connor R, Saxton K, Freeman J, Wilcox MH. Activity of vancomycin against epidemic Clostridium difficile strains in a human gut model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;63:520–5. - PubMed
-
- Freeman J, Baines SD, Saxton K, Wilcox MH. Effect of metronidazole on growth and toxin production by epidemic Clostridium difficile PCR ribotypes 001 and 027 in a human gut model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;60:83–91. - PubMed
-
- Wilson KH. The microecology of Clostridium difficile. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;16(Suppl 4):S214–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

