Direct and indirect involvement of microRNA-499 in clinical and experimental cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 22752967
- PMCID: PMC3429338
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.265736
Direct and indirect involvement of microRNA-499 in clinical and experimental cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Rationale: MicroRNA-499 and other members of the myomiR family regulate myosin isoforms in pressure-overload hypertrophy. miR-499 expression varies in human disease, but results of mouse cardiac miR-499 overexpression are inconsistent, either protecting against ischemic damage or aggravating cardiomyopathy after pressure overload. Likewise, there is disagreement over direct and indirect cardiac mRNAs targeted in vivo by miR-499.
Objective: To define the associations between regulated miR-499 level in clinical and experimental heart disease and modulation of its predicted mRNA targets and to determine the consequences of increased cardiac miR-499 on direct mRNA targeting, indirect mRNA modulation, and on myocardial protein content and posttranslational modification.
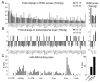
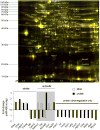
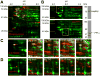
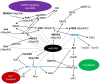
Methods and results: miR-499 levels were increased in failing and hypertrophied human hearts and associated with decreased levels of predicted target mRNAs. Likewise, miR-499 is increased in Gq-mediated murine cardiomyopathy. Forced cardiomyocyte expression of miR-499 at levels comparable to human cardiomyopathy induced progressive murine heart failure and exacerbated cardiac remodeling after pressure overloading. Genome-wide RNA-induced silencing complex and RNA sequencing identified 67 direct, and numerous indirect, cardiac mRNA targets, including Akt and MAPKs. Myocardial proteomics identified alterations in protein phosphorylation linked to the miR-499 cardiomyopathy phenotype, including of heat shock protein 90 and protein serine/threonine phosphatase 1-α.
Conclusions: miR-499 is increased in human and murine cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyopathy, is sufficient to cause murine heart failure, and accelerates maladaptation to pressure overloading. The deleterious effects of miR-499 reflect the cumulative consequences of direct and indirect mRNA regulation, modulation of cardiac kinase and phosphatase pathways, and higher-order effects on posttranslational modification of myocardial proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest relating to this manuscript.
Figures
Comment in
-
Targeting microRNA targets.Circ Res. 2012 Aug 17;111(5):506-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.276717. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22904037 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wang JX, Jiao JQ, Li Q, Long B, Wang K, Liu JP, Li YR, Li PF. miR-499 regulates mitochondrial dynamics by targeting calcineurin and dynamin-related protein-1. Nat Med. 2011;17:71–78. - PubMed
-
- Matkovich SJ, Van Booven DJ, Youker KA, Torre-Amione G, Diwan A, Eschenbacher WH, Dorn LE, Watson MA, Margulies KB, Dorn GW., 2nd Reciprocal regulation of myocardial microRNAs and messenger RNA in human cardiomyopathy and reversal of the microRNA signature by biomechanical support. Circulation. 2009;119:1263–1271. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

