Synthetic motility and cell shape defects associated with deletions of flotillin/reggie paralogs in Bacillus subtilis and interplay of these proteins with NfeD proteins
- PMID: 22753055
- PMCID: PMC3415494
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00910-12
Synthetic motility and cell shape defects associated with deletions of flotillin/reggie paralogs in Bacillus subtilis and interplay of these proteins with NfeD proteins
Abstract
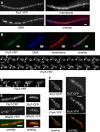
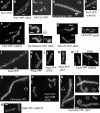
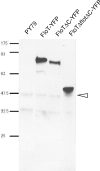
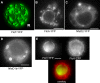
Flotillin/reggie proteins are membrane-associated proteins present in all kinds of cells and belong to the family of proteins carrying the SPFH (stomatin, prohibitin, flotillin, and HflK/HflC) domain. In addition to this domain of unknown function, flotillin proteins are characterized by the flotillin domain, which is rich in heptad repeats. Bacterial flotillin orthologs have recently been shown to be part of lipid rafts, like their eukaryotic counterparts, and to be involved in signaling events. Double deletions of floT and the gene encoding the second flotillin-like protein in Bacillus subtilis, floA, show strong synthetic defects in cell morphology, motility, and transformation efficiency. The lack of FloT resulted in a marked defect in motility. Using total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy, we show that both proteins localize in characteristic focal structures within the cell membrane, which move in a highly dynamic and random manner but localize independently of each other. Thus, flotillin paralogs act in a spatially distinct manner. Flotillin domains in both FloA and FloT are essential for focal assemblies and for the proper function of flotillins. Both flotillin genes are situated next to genes encoding NfeD proteins. FloT dramatically affects the localization of NfeD2: FloT apparently recruits NfeD2 into the focal assemblies, documenting a close interaction between flotillins and NfeDs in bacteria. In contrast, the localization of NfeD1b is not affected by FloA, FloT, or NfeD2. FloA does not show a spatial connection with the upstream-encoded NfeD1b (YqeZ). Our work establishes that bacterial flotillin-like proteins have overlapping functions in a variety of membrane-associated processes and that flotillin domain-mediated assembly and NfeD proteins play important roles in setting up the flotillin raft-like structures in vivo.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Super Resolution Fluorescence Microscopy and Tracking of Bacterial Flotillin (Reggie) Paralogs Provide Evidence for Defined-Sized Protein Microdomains within the Bacterial Membrane but Absence of Clusters Containing Detergent-Resistant Proteins.PLoS Genet. 2016 Jun 30;12(6):e1006116. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006116. eCollection 2016 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27362352 Free PMC article.
-
The deletion of bacterial dynamin and flotillin genes results in pleiotrophic effects on cell division, cell growth and in cell shape maintenance.BMC Microbiol. 2012 Dec 19;12:298. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-298. BMC Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23249255 Free PMC article.
-
The lipid raft markers stomatin, prohibitin, flotillin, and HflK/C (SPFH)-domain proteins form an operon with NfeD proteins and function with apolar polyisoprenoid lipids.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020 Feb;46(1):38-48. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2020.1716682. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31983249 Review.
-
Scaffolding microdomains and beyond: the function of reggie/flotillin proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Oct;62(19-20):2228-40. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-5166-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 16091845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ancient origin of reggie (flotillin), reggie-like, and other lipid-raft proteins: convergent evolution of the SPFH domain.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006 Feb;63(3):343-57. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-5434-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16389450 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Flotillin-mediated stabilization of unfolded proteins in bacterial membrane microdomains.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 3;15(1):5583. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49951-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38961085 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Antibacterial Mechanisms of the Pioneering Peptide Antibiotics Tyrocidine and Gramicidin S.mBio. 2018 Oct 9;9(5):e00802-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00802-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30301848 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuating Staphylococcus aureus Virulence by Targeting Flotillin Protein Scaffold Activity.Cell Chem Biol. 2017 Jul 20;24(7):845-857.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.05.027. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Cell Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28669526 Free PMC article.
-
Overproduction of flotillin influences cell differentiation and shape in Bacillus subtilis.mBio. 2013 Nov 12;4(6):e00719-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00719-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 24222488 Free PMC article.
-
The phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system is involved in sensitivity to the glucosylated bacteriocin sublancin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Nov;59(11):6844-54. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01519-15. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26282429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babuke T, Tikkanen R. 2007. Dissecting the molecular function of reggie/flotillin proteins. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 86:525–532 - PubMed
-
- Bickel PE, et al. 1997. Flotillin and epidermal surface antigen define a new family of caveolae-associated integral membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 272:13793–13802 - PubMed
-
- Browman DT, Hoegg MB, Robbins SM. 2007. The SPFH domain-containing proteins: more than lipid raft markers. Trends Cell Biol. 17:394–402 - PubMed
-
- Cao M, et al. 2002. Defining the Bacillus subtilis sigma(W) regulon: a comparative analysis of promoter consensus search, run-off transcription/macroarray analysis (ROMA), and transcriptional profiling approaches. J. Mol. Biol. 316:443–457 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

