Pseudomonas aeruginosa directly shunts β-oxidation degradation intermediates into de novo fatty acid biosynthesis
- PMID: 22753057
- PMCID: PMC3457203
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00860-12
Pseudomonas aeruginosa directly shunts β-oxidation degradation intermediates into de novo fatty acid biosynthesis
Abstract
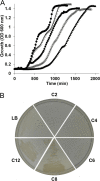
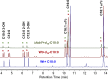
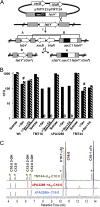
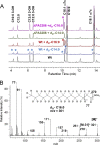
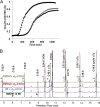
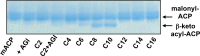
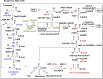
We identified the fatty acid synthesis (FAS) initiation enzyme in Pseudomonas aeruginosa as FabY, a β-ketoacyl synthase KASI/II domain-containing enzyme that condenses acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) with malonyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) to make the FAS primer β-acetoacetyl-ACP in the accompanying article (Y. Yuan, M. Sachdeva, J. A. Leeds, and T. C. Meredith, J. Bacteriol. 194:5171-5184, 2012). Herein, we show that growth defects stemming from deletion of fabY can be suppressed by supplementation of the growth media with exogenous decanoate fatty acid, suggesting a compensatory mechanism. Fatty acids eight carbons or longer rescue growth by generating acyl coenzyme A (acyl-CoA) thioester β-oxidation degradation intermediates that are shunted into FAS downstream of FabY. Using a set of perdeuterated fatty acid feeding experiments, we show that the open reading frame PA3286 in P. aeruginosa PAO1 intercepts C(8)-CoA by condensation with malonyl-ACP to make the FAS intermediate β-keto decanoyl-ACP. This key intermediate can then be extended to supply all of the cellular fatty acid needs, including both unsaturated and saturated fatty acids, along with the 3-hydroxyl fatty acid acyl groups of lipopolysaccharide. Heterologous PA3286 expression in Escherichia coli likewise established the fatty acid shunt, and characterization of recombinant β-keto acyl synthase enzyme activity confirmed in vitro substrate specificity for medium-chain-length acyl CoA thioester acceptors. The potential for the PA3286 shunt in P. aeruginosa to curtail the efficacy of inhibitors targeting FabY, an enzyme required for FAS initiation in the absence of exogenous fatty acids, is discussed.
Figures

Comment in
-
Will the initiator of fatty acid synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa please stand up?J Bacteriol. 2012 Oct;194(19):5159-61. doi: 10.1128/JB.01198-12. Epub 2012 Jul 20. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22821980 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Fatty acid biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is initiated by the FabY class of β-ketoacyl acyl carrier protein synthases.J Bacteriol. 2012 Oct;194(19):5171-84. doi: 10.1128/JB.00792-12. Epub 2012 Jun 29. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22753059 Free PMC article.
-
Ralstonia solanacearum RSp0194 Encodes a Novel 3-Keto-Acyl Carrier Protein Synthase III.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 25;10(8):e0136261. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136261. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26305336 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity in fatty acid elongation enzymes: The FabB long-chain β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase I initiates fatty acid synthesis in Pseudomonas putida F1.J Biol Chem. 2024 Feb;300(2):105600. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105600. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38335573 Free PMC article.
-
The Escherichia coli FadR transcription factor: Too much of a good thing?Mol Microbiol. 2021 Jun;115(6):1080-1085. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14663. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Mol Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33283913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional organization of the animal fatty acid synthase.Prog Lipid Res. 2003 Jul;42(4):289-317. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7827(02)00067-x. Prog Lipid Res. 2003. PMID: 12689621 Review.
Cited by
-
An atypical 3-ketoacyl ACP synthase III required for acyl homoserine lactone synthesis in Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae B728a.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Mar 20;90(3):e0225623. doi: 10.1128/aem.02256-23. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38415624 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial lyso-form lipoproteins are synthesized via an intramolecular acyl chain migration.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 24;295(30):10195-10211. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014000. Epub 2020 May 29. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32471867 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics responses and tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa under acoustic vibration stress.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 29;19(1):e0297030. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297030. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38285708 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Xanthomonas campestris Long-Chain-Specific 3-Oxoacyl-Acyl Carrier Protein Reductase Involved in Diffusible Signal Factor Synthesis.mBio. 2018 May 8;9(3):e00596-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00596-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29739899 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acid biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is initiated by the FabY class of β-ketoacyl acyl carrier protein synthases.J Bacteriol. 2012 Oct;194(19):5171-84. doi: 10.1128/JB.00792-12. Epub 2012 Jun 29. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22753059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Black PN, DiRusso CC. 1994. Molecular and biochemical analyses of fatty acid transport, metabolism, and gene regulation in Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1210:123–145 - PubMed
-
- Breidenstein EB, Fuente-Nunez C, Hancock RE. 2011. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: all roads lead to resistance. Trends Microbiol. 19:419–426 - PubMed
-
- Brinster S, et al. 2009. Type II fatty acid synthesis is not a suitable antibiotic target for Gram-positive pathogens. Nature 458:83–86 - PubMed
-
- Brown AK, et al. 2005. Probing the mechanism of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis beta-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III mtFabH: factors influencing catalysis and substrate specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 280:32539–32547 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

