Transcriptional cross talk within the mar-sox-rob regulon in Escherichia coli is limited to the rob and marRAB operons
- PMID: 22753060
- PMCID: PMC3430332
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00680-12
Transcriptional cross talk within the mar-sox-rob regulon in Escherichia coli is limited to the rob and marRAB operons
Abstract
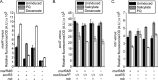
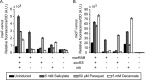
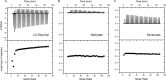
Bacteria possess multiple mechanisms to survive exposure to various chemical stresses and antimicrobial compounds. In the enteric bacterium Escherichia coli, three homologous transcription factors-MarA, SoxS, and Rob-play a central role in coordinating this response. Three separate systems are known to regulate the expression and activities of MarA, SoxS, and Rob. However, a number of studies have shown that the three do not function in isolation but rather are coregulated through transcriptional cross talk. In this work, we systematically investigated the extent of transcriptional cross talk in the mar-sox-rob regulon. While the three transcription factors were found to have the potential to regulate each other's expression when ectopically expressed, the only significant interactions observed under physiological conditions were between mar and rob systems. MarA, SoxS, and Rob all activate the marRAB promoter, more so when they are induced by their respective inducers: salicylate, paraquat, and decanoate. None of the three proteins affects the soxS promoter, though unexpectedly, it was mildly repressed by decanoate by an unknown mechanism. SoxS is the only one of the three proteins to repress the rob promoter. Surprisingly, salicylate somewhat activates transcription of rob, while decanoate represses it a bit. Rob, in turn, activates not only its downstream promoters in response to salicylate but also the marRAB promoter. These results demonstrate that the mar and rob systems function together in response to salicylate.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MarRA, SoxSR, and Rob encode a signal dependent regulatory network in Escherichia coli.Mol Biosyst. 2016 May 24;12(6):1901-12. doi: 10.1039/c6mb00263c. Mol Biosyst. 2016. PMID: 27098660
-
An excretory function for the Escherichia coli outer membrane pore TolC: upregulation of marA and soxS transcription and Rob activity due to metabolites accumulated in tolC mutants.J Bacteriol. 2009 Aug;191(16):5283-92. doi: 10.1128/JB.00507-09. Epub 2009 Jun 5. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19502391 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug Resistance Regulators MarA, SoxS, Rob, and RamA Repress Flagellar Gene Expression and Motility in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2019 Nov 5;201(23):e00385-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00385-19. Print 2019 Dec 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31501286 Free PMC article.
-
The Mar, Sox, and Rob Systems.EcoSal Plus. 2023 Dec 12;11(1):eesp00102022. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.esp-0010-2022. Epub 2023 Apr 4. EcoSal Plus. 2023. PMID: 37220096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Escherichia coli multiple antibiotic resistance activator protein represses transcription of the lac operon.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Apr 30;47(2):671-677. doi: 10.1042/BST20180498. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 30850424 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenotypic and Multi-Omics Characterization of Escherichia coli K-12 Adapted to Chlorhexidine Identifies the Role of MlaA and Other Cell Envelope Alterations Regulated by Stress Inducible Pathways in CHX Resistance.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 19;8:659058. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.659058. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34095221 Free PMC article.
-
Species-specific activity of antibacterial drug combinations.Nature. 2018 Jul;559(7713):259-263. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0278-9. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29973719 Free PMC article.
-
Customized Regulation of Diverse Stress Response Genes by the Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Activator MarA.PLoS Comput Biol. 2017 Jan 6;13(1):e1005310. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005310. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017. PMID: 28060821 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional response of mar, sox and rob regulon against concentration gradient carbapenem stress within Escherichia coli isolated from hospital acquired infection.BMC Res Notes. 2020 Mar 19;13(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s13104-020-04999-2. BMC Res Notes. 2020. PMID: 32192538 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Regulation of the Multiple Resistance Mechanisms in Salmonella-A Review.Pathogens. 2021 Jun 24;10(7):801. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10070801. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34202800 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alekshun MN, Levy SB. 2007. Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell 128:1037–1050 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

