Integrated Hedgehog signaling is induced following castration in human and murine prostate cancers
- PMID: 22753310
- PMCID: PMC3878994
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.22550
Integrated Hedgehog signaling is induced following castration in human and murine prostate cancers
Abstract
Background: The interplay between androgen and Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathways may be associated with prostate cancer progression and resistance to therapy.
Methods: Tissue microarrays from prostatectomy specimens were derived from 53 patients treated preoperatively with androgen ablation (AA) with or without chemotherapy, and from 26 stage- and grade-matched controls. A previously characterized androgen-regulated human prostate cancer xenograft was used to conduct parallel murine studies. Expression of markers of interest was determined on both untreated and castrated tumors.
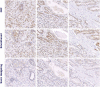
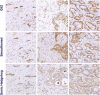
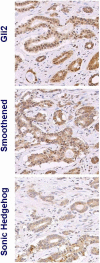
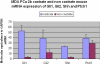
Results: Four-month exposure to AA or AA with chemotherapy led to a uniform increase in Hh signaling as compared to controls, paired with an inverse trend of androgen receptor (AR) and CYP17 expression in clinically derived specimens. Changes in the expression profiles of Hh signaling were observed in the epithelium and stroma, in response to genotoxic stress of androgen ablation and chemotherapy. A reduced expression of KI67 and increased bcl2 expression was observed in the malignant epithelial compartment.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first clinical evidence that Hh signaling is induced by AA or the combination of AA and chemotherapy and, by inference, contributes to castrate-resistant progression of prostate cancer as supported by parallel human and murine studies. These data are in agreement with previous reports that implicate Hh signaling in castrate-resistant progression of prostate cancer. Based on these findings, we are pursuing parallel clinical and murine investigations to determine if Hh signaling inhibition combined with AA will be more effective than AA alone.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hedgehog signaling inhibition by the small molecule smoothened inhibitor GDC-0449 in the bone forming prostate cancer xenograft MDA PCa 118b.Prostate. 2012 Nov;72(15):1638-47. doi: 10.1002/pros.22517. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Prostate. 2012. PMID: 22457212 Free PMC article.
-
TAK-441, a novel investigational smoothened antagonist, delays castration-resistant progression in prostate cancer by disrupting paracrine hedgehog signaling.Int J Cancer. 2013 Oct 15;133(8):1955-66. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28193. Epub 2013 May 6. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23564295
-
Sox2 is an androgen receptor-repressed gene that promotes castration-resistant prostate cancer.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053701. Epub 2013 Jan 11. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23326489 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular biology of castration-resistant prostate cancer: basis for the novel therapeutic targets.Arch Esp Urol. 2013 Jun;66(5):453-62. Arch Esp Urol. 2013. PMID: 23793763 Review.
-
Oxidative stress and androgen receptor signaling in the development and progression of castration-resistant prostate cancer.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Oct 1;51(7):1320-8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.07.011. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21820046 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Gli1-mediated prostate cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2017 Dec;14(6):7970-7976. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7254. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29250185 Free PMC article.
-
Patched 1 Expression Correlates with Biochemical Relapse in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients.Am J Pathol. 2018 Mar;188(3):795-804. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.11.019. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Am J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29339090 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative integration between HEDGEHOG-GLI signalling and other oncogenic pathways: implications for cancer therapy.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015 Feb 9;17:e5. doi: 10.1017/erm.2015.3. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25660620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hedgehog signaling in prostate cancer and its therapeutic implication.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 4;14(7):13979-4007. doi: 10.3390/ijms140713979. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23880852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signalling pathways in a nutshell: from pathogenesis to therapeutical implications in prostate cancer.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2474175. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2474175. Epub 2025 May 15. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40372974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Attard G, Reid AH, Olmos D, de Bono JS. Antitumor activity with CYP17 blockade indicates that castration-resistant prostate cancer frequently remains hormone driven. Cancer Res. 2009;69(12):4937–4940. - PubMed
-
- Stanbrough M, Bubley GJ, Ross K, Golub TR, Rubin MA, Penning TM, Febbo PG, Balk SP. Increased expression of genes converting adrenal androgens to testosterone in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66(5):2815–2825. - PubMed
-
- Karhadkar SS, Bova GS, Abdallah N, Dhara S, Gardner D, Maitra A, Isaacs JT, Berman DM, Beachy PA. Hedgehog signalling in prostate regeneration, neoplasia and metastasis. Nature. 2004;431(7009):707–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

