Suppression of nuclear factor-κB activation and inflammation in microglia by physically modified saline
- PMID: 22753407
- PMCID: PMC3436140
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.338012
Suppression of nuclear factor-κB activation and inflammation in microglia by physically modified saline
Abstract
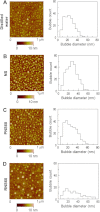
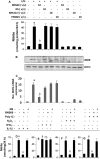
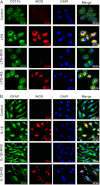
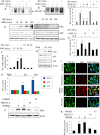
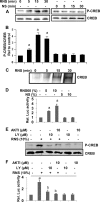
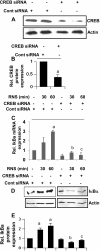
Chronic inflammation involving activated microglia and astroglia is becoming a hallmark of many human diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders. Although NF-κB is a multifunctional transcription factor, it is an important target for controlling inflammation as the transcription of many proinflammatory molecules depends on the activation of NF-κB. Here, we have undertaken a novel approach to attenuate NF-κB activation and associated inflammation in activated glial cells. RNS60 is a 0.9% saline solution containing charge-stabilized nanostructures that are generated by subjecting normal saline to Taylor-Couette-Poiseuille (TCP) flow under elevated oxygen pressure. RNS60, but not normal saline, RNS10.3 (TCP-modified saline without excess oxygen), and PNS60 (saline containing excess oxygen without TCP modification) were found to inhibit the production of nitric oxide (NO) and the expression of inducible NO synthase in activated microglia. Similarly, RNS60 also inhibited the expression of inducible NO synthase in activated astroglia. Inhibition of NF-κB activation by RNS60 suggests that RNS60 exerts its anti-inflammatory effect through the inhibition of NF-κB. Interestingly, RNS60 induced the activation of type IA phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase and Akt and rapidly up-regulated IκBα, a specific endogenous inhibitor of NF-κB. Inhibition of PI 3-kinase and Akt by either chemical inhibitors or dominant-negative mutants abrogated the RNS60-mediated up-regulation of IκBα. Furthermore, we demonstrate that RNS60 induced the activation of cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) via the PI 3-kinase-Akt pathway and that RNS60 up-regulated IκBα via CREB. These results describe a novel anti-inflammatory property of RNS60 via type IA PI 3-kinase-Akt-CREB-mediated up-regulation of IκBα, which may be of therapeutic benefit in neurodegenerative disorders.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Upregulation of Myelin Gene Expression by a Physically-Modified Saline via Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-Mediated Activation of CREB: Implications for Multiple Sclerosis.Neurochem Res. 2018 Feb;43(2):407-419. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2435-1. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29143164 Free PMC article.
-
Increase in Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Neuronal Cells by RNS60, a Physically-Modified Saline, via Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-Mediated Upregulation of PGC1α.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;13(2):143-162. doi: 10.1007/s11481-017-9771-4. Epub 2017 Nov 29. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29188424 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of morphological plasticity in hippocampal neurons by a physically modified saline via phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 9;9(7):e101883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101883. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25007337 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB as an Inducible Regulator of Inflammation in the Central Nervous System.Cells. 2024 Mar 11;13(6):485. doi: 10.3390/cells13060485. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase gene in glial cells.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006 May-Jun;8(5-6):929-47. doi: 10.1089/ars.2006.8.929. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006. PMID: 16771683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stimulation of Dopamine Production by Sodium Benzoate, a Metabolite of Cinnamon and a Food Additive.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2021 Apr 23;5(1):295-310. doi: 10.3233/ADR-210001. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2021. PMID: 34113786 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3 in Microglia by Cinnamic Acid.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2018;15(10):894-904. doi: 10.2174/1567205015666180507104755. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2018. PMID: 29732971 Free PMC article.
-
Apparent Km of mitochondria for oxygen computed from Vmax measured in permeabilized muscle fibers is lower in water enriched in oxygen by electrolysis than injection.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jul 13;9:3589-97. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S81891. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26203225 Free PMC article.
-
Omarigliptin Mitigates 6-Hydroxydopamine- or Rotenone-Induced Oxidative Toxicity in PC12 Cells by Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Actions.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;11(10):1940. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101940. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290663 Free PMC article.
-
RNS60 exerts therapeutic effects in the SOD1 ALS mouse model through protective glia and peripheral nerve rescue.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Mar 1;15(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1101-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29495962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giovannini M. G., Scali C., Prosperi C., Bellucci A., Vannucchi M. G., Rosi S., Pepeu G., Casamenti F. (2002) β-Amyloid-induced inflammation and cholinergic hypofunction in the rat brain in vivo. Involvement of the p38MAPK pathway. Neurobiol. Dis. 11, 257–274 - PubMed
-
- Dauer W., Przedborski S. (2003) Parkinson disease. Mechanisms and models. Neuron 39, 889–909 - PubMed
-
- Gao H. M., Liu B., Zhang W., Hong J. S. (2003) Novel anti-inflammatory therapy for Parkinson disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 395–401 - PubMed
-
- Barnum C. J., Tansey M. G. (2010) Modeling neuroinflammatory pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. Prog. Brain Res. 184, 113–132 - PubMed
-
- Jantaratnotai N., Ryu J. K., Kim S. U., McLarnon J. G. (2003) Amyloid β peptide-induced corpus callosum damage and glial activation in vivo. Neuroreport 14, 1429–1433 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

