Avibactam is a covalent, reversible, non-β-lactam β-lactamase inhibitor
- PMID: 22753474
- PMCID: PMC3406822
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1205073109
Avibactam is a covalent, reversible, non-β-lactam β-lactamase inhibitor
Abstract
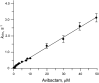
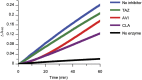
Avibactam is a β-lactamase inhibitor that is in clinical development, combined with β-lactam partners, for the treatment of bacterial infections comprising gram-negative organisms. Avibactam is a structural class of inhibitor that does not contain a β-lactam core but maintains the capacity to covalently acylate its β-lactamase targets. Using the TEM-1 enzyme, we characterized avibactam inhibition by measuring the on-rate for acylation and the off-rate for deacylation. The deacylation off-rate was 0.045 min(-1), which allowed investigation of the deacylation route from TEM-1. Using NMR and MS, we showed that deacylation proceeds through regeneration of intact avibactam and not hydrolysis. Other than TEM-1, four additional clinically relevant β-lactamases were shown to release intact avibactam after being acylated. We showed that avibactam is a covalent, slowly reversible inhibitor, which is a unique mechanism of inhibition among β-lactamase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: All authors are present or past employees of AstraZeneca, as stated in the affiliations, and potentially own stock and/or hold stock options in the company.
Figures





References
-
- Arias CA, Murray BE. Antibiotic-resistant bugs in the 21st century—a clinical super-challenge. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:439–443. - PubMed
-
- Nordmann P, Poirel L, Toleman MA, Walsh TR. Does broad-spectrum β-lactam resistance due to NDM-1 herald the end of the antibiotic era for treatment of infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria? J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:689–692. - PubMed
-
- Bush K, Fisher JF. Epidemiological expansion, structural studies, and clinical challenges of new β-lactamases from gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2011;65:455–478. - PubMed
-
- Bebrone C, et al. Current challenges in antimicrobial chemotherapy: Focus on ß-lactamase inhibition. Drugs. 2010;70:651–679. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

