Augmenting muscle diacylglycerol and triacylglycerol content by blocking fatty acid oxidation does not impede insulin sensitivity
- PMID: 22753483
- PMCID: PMC3406830
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1206868109
Augmenting muscle diacylglycerol and triacylglycerol content by blocking fatty acid oxidation does not impede insulin sensitivity
Abstract
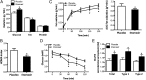
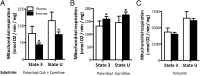
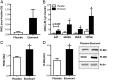
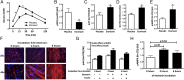
A low fat oxidative capacity has been linked to muscle diacylglycerol (DAG) accumulation and insulin resistance. Alternatively, a low fat oxidation rate may stimulate glucose oxidation, thereby enhancing glucose disposal. Here, we investigated whether an ethyl-2-[6-(4-chlorophenoxy)hexyl]-oxirane-2-carboxylate (etomoxir)-induced inhibition of fat oxidation leads to muscle fat storage and insulin resistance. An intervention in healthy male subjects was combined with studies in human primary myotubes. Furthermore, muscle DAG and triacylglycerol (TAG), mitochondrial function, and insulin signaling were examined in etomoxir-treated C57bl6 mice. In humans, etomoxir administration increased glucose oxidation at the expense of fat oxidation. This effect was accompanied by an increased abundance of GLUT4 at the sarcolemma and a lowering of plasma glucose levels, indicative of improved glucose homeostasis. In mice, etomoxir injections resulted in accumulation of muscle TAG and DAG, yet improved insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation. Also in human myotubes, insulin signaling was improved by etomoxir, in the presence of increased intramyocellular lipid accumulation. These insulin-sensitizing effects in mice and human myotubes were accompanied by increased phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Our results show that a reduction in fat oxidation leading to accumulation of muscle DAG does not necessarily lead to insulin resistance, as the reduction in fat oxidation may activate AMPK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Boden G, Lebed B, Schatz M, Homko C, Lemieux S. Effects of acute changes of plasma free fatty acids on intramyocellular fat content and insulin resistance in healthy subjects. Diabetes. 2001;50:1612–1617. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann OP, et al. Effects of intravenous and dietary lipid challenge on intramyocellular lipid content and the relation with insulin sensitivity in humans. Diabetes. 2001;50:2579–2584. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA, et al. The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes. 1981;30:1000–1007. - PubMed
-
- Baron AD, Brechtel G, Wallace P, Edelman SV. Rates and tissue sites of non-insulin- and insulin-mediated glucose uptake in humans. Am J Physiol. 1988;255:E769–E774. - PubMed
-
- Randle PJ, Garland PB, Hales CN, Newsholme EA. The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1963;1:785–789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

