Energy balance and obesity
- PMID: 22753534
- PMCID: PMC3401553
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.087213
Energy balance and obesity
Abstract
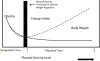
This paper describes the interplay among energy intake, energy expenditure and body energy stores and illustrates how an understanding of energy balance can help develop strategies to reduce obesity. First, reducing obesity will require modifying both energy intake and energy expenditure and not simply focusing on either alone. Food restriction alone will not be effective in reducing obesity if human physiology is biased toward achieving energy balance at a high energy flux (i.e. at a high level of energy intake and expenditure). In previous environments a high energy flux was achieved with a high level of physical activity but in today's sedentary environment it is increasingly achieved through weight gain. Matching energy intake to a high level of energy expenditure will likely be more a more feasible strategy for most people to maintain a healthy weight than restricting food intake to meet a low level of energy expenditure. Second, from an energy balance point of view we are likely to be more successful in preventing excessive weight gain than in treating obesity. This is because the energy balance system shows much stronger opposition to weight loss than to weight gain. While large behavior changes are needed to produce and maintain reductions in body weight, small behavior changes may be sufficient to prevent excessive weight gain. In conclusion, the concept of energy balance combined with an understanding of how the body achieves balance may be a useful framework in helping develop strategies to reduce obesity rates.
Figures
References
-
- Hill JO, Levine JS, Saris WHM. Energy expenditure and physical activity. In: Bray G, Bouchard C, editors. Handbook of Obesity. Second Edition Marcel Dekker, Inc; New York, N.Y.: 2003. pp. 631–654.
-
- Hill JO, Commerford R. Exercise, fat balance and energy balance. International Journal of Sports Nutrition. 1996;6:80–92. - PubMed
-
- Sandoval D, Cota D, Seeley RJ. The Integrative Role of CNS Fuel-Sensing Mechanisms in Energy Balance and Glucose Regulation. Ann Rev Physiology. 2008;70:513–535. - PubMed
-
- Horton TJ, Drougas H, Brachey A, Reed GW, Peters JC, Hill JO. Fat and carbohydrate overfeeding in humans: different effects on energy storage. Am Clin Nutr. 1995;62:19–29. - PubMed
-
- Blundell JE, Stubbs RJ, Hughes DA, Whybrow S, King NA. Cross talk between physical activity and appetite control: does physical activity stimulate appetite? Proceedings of the Nutrition Society. 2003;62:651–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

