Sequential interaction of chloride and proton ions with the fast gate steer the voltage-dependent gating in ClC-2 chloride channels
- PMID: 22753549
- PMCID: PMC3473282
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.232660
Sequential interaction of chloride and proton ions with the fast gate steer the voltage-dependent gating in ClC-2 chloride channels
Abstract
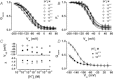
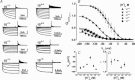
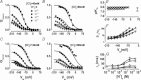
The interaction of either H(+) or Cl(-) ions with the fast gate is the major source of voltage (V(m)) dependence in ClC Cl(-) channels. However, the mechanism by which these ions confer V(m) dependence to the ClC-2 Cl(-) channel remains unclear. By determining the V(m) dependence of normalized conductance (G(norm)(V(m))), an index of open probability, ClC-2 gating was studied at different [H(+)](i), [H(+)](o) and [Cl(-)](i). Changing [H(+)](i) by five orders of magnitude whilst [Cl(-)](i)/[Cl(-)](o) = 140/140 or 10/140 mm slightly shifted G(norm)(V(m)) to negative V(m) without altering the onset kinetics; however, channel closing was slower at acidic pH(i). A similar change in [H(+)](o) with [Cl(-)](i)/[Cl(-)](o) = 140/140 mm enhanced G(norm) in a bell-shaped manner and shifted G(norm)(V(m)) curves to positive V(m). Importantly, G(norm) was >0 with [H(+)](o) = 10(-10) m but channel closing was slower when [H(+)](o) or [Cl(-)](i) increased implying that ClC-2 was opened without protonation and that external H(+) and/or internal Cl(-) ions stabilized the open conformation. The analysis of kinetics and steady-state properties at different [H(+)](o) and [Cl(-)](i) was carried out using a gating Scheme coupled to Cl(-) permeation. Unlike previous results showing V(m)-dependent protonation, our analysis revealed that fast gate protonation was V(m) and Cl(-) independent and the equilibrium constant for closed–open transition of unprotonated channels was facilitated by elevated [Cl(-)](i) in a V(m)-dependent manner. Hence a V(m) dependence of pore occupancy by Cl(-) induces a conformational change in unprotonated closed channels, before the pore opens, and the open conformation is stabilized by Cl(-) occupancy and V(m)-independent protonation.
Figures

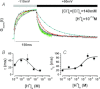
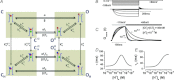
 is indicated by a blue sphere attach to a red sphere. Transitions between Cl−-free and Cl−-bound states are dictated by Vm-dependent rate constants. Transitions between unprotonated and protonated states are characterized by Vm-independent equilibrium constants
is indicated by a blue sphere attach to a red sphere. Transitions between Cl−-free and Cl−-bound states are dictated by Vm-dependent rate constants. Transitions between unprotonated and protonated states are characterized by Vm-independent equilibrium constants  and KO, respectively. Fast gate is open by electrostatic repulsion when either a Cl− (f1 = 151) or H+ ion is bound (fH = 8.46). B, simulated ionic currents from +60 mV to −180 mV, in 40 mV increments according to the voltage protocol shown on top. ICl(t) were simulated for [Cl−]i = [Cl−]o = 140 m
and KO, respectively. Fast gate is open by electrostatic repulsion when either a Cl− (f1 = 151) or H+ ion is bound (fH = 8.46). B, simulated ionic currents from +60 mV to −180 mV, in 40 mV increments according to the voltage protocol shown on top. ICl(t) were simulated for [Cl−]i = [Cl−]o = 140 m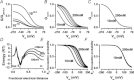
References
-
- Bezanilla F. How membrane proteins sense voltage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:323–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

