A receptor-targeted fluorescent radiopharmaceutical for multireporter sentinel lymph node imaging
- PMID: 22753678
- PMCID: PMC3447170
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.12120638
A receptor-targeted fluorescent radiopharmaceutical for multireporter sentinel lymph node imaging
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the imaging and receptor-binding properties of a multireporter probe designed for sentinel lymph node (SLN) mapping via nuclear and fluorescence detection.
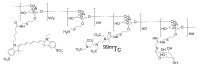
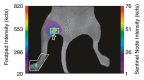
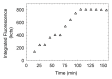
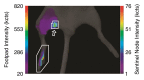
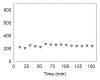
Materials and methods: The animal experiments were approved by the institutional animal care and use committee. A multireporter probe was synthesized by covalently attaching cyanine 7 (Cy7), a near-infrared cyanine dye, to tilmanocept, a radiopharmaceutical that binds to a receptor specific to recticuloendothelial cells. In vitro binding assays of technetium 99m (99mTc)-labeled Cy7 tilmanocept were conducted at 4°C by using receptor-bearing macrophages. Optical SLN imaging after foot pad administration was performed by using two molar doses of Cy7 tilmanocept. Six mice were injected with 0.11 nmol of 99mTc-labeled Cy7 tilmanocept (low-dose group); an additional six mice were injected with 31 nmol of 99mTc-labeled Cy7 tilmanocept (high-dose group) to saturate the receptor sites within the SLN. After 2.5 hours of imaging, the mice were euthanized, and the sentinel and distal lymph nodes were excised and assayed for radioactivity for calculation of SLN percentage of injected dose and extraction. Four mice were used as controls for autofluorescence. Standard optical imaging software was used to plot integrated fluorescence intensity against time for calculation of the SLN uptake rate constant and scaled peak intensity. Significance was calculated by using the Student t test.
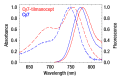
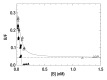
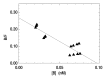
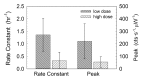
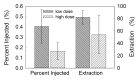
Results: In vitro binding assays showed subnanomolar affinity (mean dissociation constant, 0.25 nmol/L±0.10 [standard deviation]). Fluorescence imaging showed a detection sensitivity of 1.6×10(3) counts·sec(-1)·μW(-1) per picomole of Cy7. All four imaging metrics (percentage of injected dose, SLN extraction, SLN uptake rate constant, and expected peak fluorescence intensity) exhibited higher values (P=.005 to P=.042) in the low-dose group than in the high-dose group; this finding was consistent with receptor-mediated image formation.
Conclusion: The multireporter probe 99mTc-labeled Cy7 tilmanocept exhibits in vitro and in vivo receptor-binding properties for successful receptor-targeted SLN mapping with nuclear and optical imaging.
© RSNA, 2012.
Figures
References
-
- Morton DL, Wen D-R, Wong JH, et al. Technical details of intraoperative lymphatic mapping for early stage melanoma. Arch Surg 1992;127(4):392–399 - PubMed
-
- Krag DN, Weaver DL, Alex JC, Fairbank JT. Surgical resection and radiolocalization of the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer using a gamma probe. Surg Oncol 1993;2(6):335–339; discussion 340 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

