Effects of Zeng Sheng Ping/ACAPHA on malignant brain tumor growth and Notch signaling
- PMID: 22753727
- PMCID: PMC3575600
Effects of Zeng Sheng Ping/ACAPHA on malignant brain tumor growth and Notch signaling
Abstract
Background/aim: Zeng Sheng Ping (ZSP) is a traditional herbal remedy used to prevent progression and growth of neoplastic lesions. It has been shown to inhibit Notch2 expression in a murine lung cancer model, leading us to investigate its therapeutic potential in Notch-dependent brain tumors.
Materials and methods: 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium (MTS), apoptosis, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analyses were performed in glioma and medulloblastoma cell lines, and morphological analyses in DAOY flank xenografts.
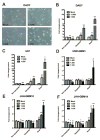
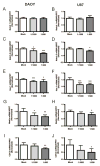
Results: ZSP inhibited brain tumor growth in vitro, in part, by apoptotic induction. Down-regulation of the Notch2 receptor, the pathway target Hairy/Enhancer of Split homolog 1 (Hes1), and of the stem cell markers Nestin and CD133 was also observed. Reductions in tumor mass and increases in the necrotic fraction of DAOY xenografts, in mice treated with oral ZSP were also observed, but these were not significant.
Conclusion: ZSP can block brain tumor growth and the expression of Notch pathway members and stem cell markers in vitro.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

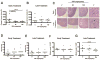
References
-
- Fan X. Inhibitory effect of antitumor-B and retinamide on precancerous lesions of the bladder in rats. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 1993;15(1):71–73. (in Chinese) - PubMed
-
- Sun Z, Guan X, Li N, Liu X, Chen X. Chemoprevention of oral cancer in animal models, and effect on leukoplakias in human patients with Zeng Sheng Ping, a mixture of medicinal herbs. Oral Oncol. 2010;46(2):105–110. - PubMed
-
- Wang J. Results of phase III clinical trial of zeng sheng-ping in the treatment of patients with esophageal epithelial hyperplasia. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2000;22(6):510–512. (in Chinese) - PubMed
-
- Lin P, Zhang J, Rong Z, Han R, Xu S, Gao R, Ding Z, Wang J, Feng H, Cao S. Studies on medicamentous inhibitory therapy for esophageal precancerous lesions--3- and 5-year inhibitory effects of antitumor-B, retinamide and riboflavin. Proc Chin Acad Med Sci Peking Union Med Coll. 1990;5(3):121–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
