Hyperfractionated or accelerated radiotherapy in lung cancer: an individual patient data meta-analysis
- PMID: 22753901
- PMCID: PMC4934452
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2012.41.6677
Hyperfractionated or accelerated radiotherapy in lung cancer: an individual patient data meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: In lung cancer, randomized trials assessing hyperfractionated or accelerated radiotherapy seem to yield conflicting results regarding the effects on overall (OS) or progression-free survival (PFS). The Meta-Analysis of Radiotherapy in Lung Cancer Collaborative Group decided to address the role of modified radiotherapy fractionation.
Material and methods: We performed an individual patient data meta-analysis in patients with nonmetastatic lung cancer, which included trials comparing modified radiotherapy with conventional radiotherapy.
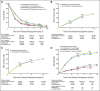
Results: In non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC; 10 trials, 2,000 patients), modified fractionation improved OS as compared with conventional schedules (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.88, 95% CI, 0.80 to 0.97; P = .009), resulting in an absolute benefit of 2.5% (8.3% to 10.8%) at 5 years. No evidence of heterogeneity between trials was found. There was no evidence of a benefit on PFS (HR = 0.94; 95% CI, 0.86 to 1.03; P = .19). Modified radiotherapy reduced deaths resulting from lung cancer (HR = 0.89; 95% CI, 0.81 to 0.98; P = .02), and there was a nonsignificant reduction of non-lung cancer deaths (HR = 0.87; 95% CI, 0.66 to 1.15; P = .33). In small-cell lung cancer (SCLC; two trials, 685 patients), similar results were found: OS, HR = 0.87, 95% CI, 0.74 to 1.02, P = .08; PFS, HR = 0.88, 95% CI, 0.75 to 1.03, P = .11. In both NSCLC and SCLC, the use of modified radiotherapy increased the risk of acute esophageal toxicity (odds ratio [OR] = 2.44 in NSCLC and OR = 2.41 in SCLC; P < .001) but did not have an impact on the risk of other acute toxicities.
Conclusion: Patients with nonmetastatic NSCLC derived a significant OS benefit from accelerated or hyperfractionated radiotherapy; a similar but nonsignificant trend was observed for SCLC. As expected, there was increased acute esophageal toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Verdecchia A, Francisci S, Brenner H, et al. Recent cancer survival in Europe: A 2000-02 period analysis of EUROCARE-4 data. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:784–796. - PubMed
-
- Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: Analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiologic, and End Results database. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4539–4544. - PubMed
-
- Stuschke M, Pöttgen C. Localized small-cell lung cancer: Which type of thoracic radiotherapy and which time schedule. Lung Cancer. 2004;45(suppl 2):S133–S137. - PubMed
-
- Arriagada R, Komaki R, Cox JD. Radiation dose escalation in non-small cell carcinoma of the lung. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2004;14:287–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

