Chronic activation of the kinase IKKβ impairs T cell function and survival
- PMID: 22753932
- PMCID: PMC3401317
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102429
Chronic activation of the kinase IKKβ impairs T cell function and survival
Abstract
Activation of the transcription factor NF-κB is critical for cytokine production and T cell survival after TCR engagement. The effects of persistent NF-κB activity on T cell function and survival are poorly understood. In this study, using a murine model that expresses a constitutively active form of inhibitor of NF-κB kinase β (caIKKβ) in a T cell-specific manner, we demonstrate that chronic inhibitor of NF-κB kinase β signaling promotes T cell apoptosis, attenuates responsiveness to TCR-mediated stimulation in vitro, and impairs T cell responses to bacterial infection in vivo. caIKKβ T cells showed increased Fas ligand expression and caspase-8 activation, and blocking Fas/Fas ligand interactions enhanced cell survival. T cell unresponsiveness was associated with defects in TCR proximal signaling and elevated levels of B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein 1, a transcriptional repressor that promotes T cell exhaustion. caIKKβ T cells also showed a defect in IL-2 production, and addition of exogenous IL-2 enhanced their survival and proliferation. Conditional deletion of B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein 1 partially rescued the sensitivity of caIKKβ T cells to TCR triggering. Furthermore, adoptively transferred caIKKβ T cells showed diminished expansion and increased contraction in response to infection with Listeria monocytogenes expressing a cognate Ag. Despite their functional defects, caIKKβ T cells readily produced proinflammatory cytokines, and mice developed autoimmunity. In contrast to NF-κB's critical role in T cell activation and survival, our study demonstrates that persistent IKK-NF-κB signaling is sufficient to impair both T cell function and survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



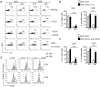
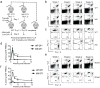
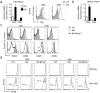

References
-
- Hayden MS, West AP, Ghosh S. NF-κB and the immune response. Oncogene. 2006;25:6758–6780. - PubMed
-
- Wang D, You Y, Case SM, McAllister-Lucas LM, Wang L, DiStefano PS, Nunez G, Bertin J, Lin X. A requirement for CARMA1 in TCR-induced NF-κB activation. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:830–835. - PubMed
-
- Wegener E, Krappmann D. CARD-Bcl10-Malt1 signalosomes: missing link to NF-κB. Sci STKE. 2007;2007:pe21. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-κB signaling. Cell. 2008;132:344–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

