The interaction of obstructive sleep apnea and obesity on the inflammatory markers C-reactive protein and interleukin-6: the Icelandic Sleep Apnea Cohort
- PMID: 22754038
- PMCID: PMC3369227
- DOI: 10.5665/sleep.1952
The interaction of obstructive sleep apnea and obesity on the inflammatory markers C-reactive protein and interleukin-6: the Icelandic Sleep Apnea Cohort
Abstract
Study objectives: To assess the relative roles and interaction of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) severity and obesity on interleukin-6 (IL-6) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels.
Design: Cross-sectional cohort.
Setting: The Icelandic Sleep Apnea Cohort.
Participants: 454 untreated OSA patients (380 males and 74 females), mean ± standard deviation age 54.4 ± 10.6 yr.
Interventions: N/A.
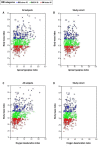
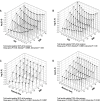
Measurements and results: Participants underwent a sleep study, abdominal magnetic resonance imaging to measure total abdominal and visceral fat volume, and had fasting morning IL-6 and CRP levels measured in serum. A significantly higher correlation was found for BMI than visceral fat volume with CRP and IL-6 levels. Oxygen desaturation index, hypoxia time, and minimum oxygen saturation (SaO₂) significantly correlated with IL-6 and CRP levels, but apnea-hypopnea index did not. When stratified by body mass index (BMI) category, OSA severity was associated with IL-6 levels in obese participants only (BMI > 30 kg/m²). A multiple linear regression model with interaction terms showed an independent association of OSA severity with IL-6 levels and an interaction between OSA severity and BMI, i.e., degree of obesity altered the relationship between OSA and IL-6 levels. An independent association of OSA severity with CRP levels was found for minimum SaO₂ only. A similar interaction of OSA severity and BMI on CRP levels was found for males and postmenopausal women.
Conclusions: OSA severity is an independent predictor of levels of IL-6 and CRP but interacts with obesity such that this association is found only in obese patients.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; Obstructive sleep apnea; interleukin-6; obesity; visceral fat.
Figures



References
-
- Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1230–5. - PubMed
-
- Ikonomidis I, Stamatelopoulos K, Lekakis J, Vamvakou GD, Kremastinos DT. Inflammatory and non-invasive vascular markers: the multimarker approach for risk stratification in coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2008;199:3–11. - PubMed
-
- Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C, et al. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006;17:4–12. - PubMed
-
- Fried SK, Bunkin DA, Greenberg AS. Omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects release interleukin-6: depot difference and regulation by glucocorticoid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83:847–50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

