Evaluation of Pistacia lentiscus fatty oil effects on glycemic index, liver functions and kidney functions of New Zealand rabbits
- PMID: 22754077
- PMCID: PMC3252718
- DOI: 10.4314/ajtcam.v8i5S.27
Evaluation of Pistacia lentiscus fatty oil effects on glycemic index, liver functions and kidney functions of New Zealand rabbits
Abstract
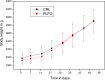
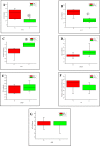
Pistacia lentiscus fatty oil (PLFO) is a well known natural remedy in eastern Algeria folk medicine. It is widely used in the treatment of respiratory disorders and dermal burns. The present study has been carried out to investigate effects of this oil on fasting glucose and some functional parameters of the liver and kidney in white male New Zealand rabbits (Initial mean weight 1.95 Kg). PLFO was applied to tested rabbits (PLFO group) via rectal route, once daily 5-day per week, for six consecutive weeks at the dose of 1 ml/Kg body weight. The same number of animals (n=6) was not treated and served as control (CRL group). The results showed that PLFO was tolerated by rectal route. No significant differences were observed in body weights of the two groups. Biochemical analysis showed that aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) were significantly decreased in blood plasma at (P< 0.05) and (P< 0.01) respectively in PLFO group (Mann-Whitney test). On the other hand, the fasting glucose level (GLU) was significantly increased (Mann-Whitney test, P< 0.05), while the rest of the tested parameters (Albumin, total proteins, creatinine, urea) was not significantly affected. However, these variations have not biologic signification toxicity. The study concludes that PLFO is tolerable via rectal route; it is safe with no adverse effect on liver functions and renal functions with possible anti-glycogenesis activity.
Keywords: LFT; Pistacia lentiscus; RFT; fatty oil; glycemic index; rabbits.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Habbal MJ, Al-Habbal Z, Huwez FU. A double-blind controlled clinical trial of mastic and placebo in the treatment of duodenal ulcer. J Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1984;11:19–23. - PubMed
-
- Ali-Shtayeh MS, Yaghmour RM, Faidi YR, Salem K, Al-Nuri M. Antimicrobial activity of 20 plants used in folkloric medicine in the Palestinian area. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 1998;60:265–271. - PubMed
-
- Archetti I, Tittarelli C, Cerioli M, Brivio R, Grilli G, Lavazza A. Serum chemistry and hematology values in commercial rabbits: Preliminary data from industrial farms in northern Italy; 9th World Rabbit Congress; June 1013, 2008; Verrona-Italy. 2008. pp. 1147–1151.
-
- Benhammou N, Atik Bekkara F, Panovska TK. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the Pistacia lentiscus and atlantica extracts. African Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2008;2(2):022–028.
-
- Bentley RY, Trimen H. Medicinal plants. London: J. and A Churchill; 1980. p. 68.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
