Anti-TNF-α activity of Portulaca oleracea in vascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 22754320
- PMCID: PMC3382818
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms13055628
Anti-TNF-α activity of Portulaca oleracea in vascular endothelial cells
Abstract
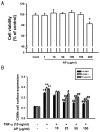
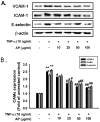
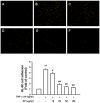
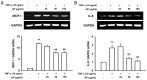
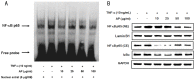
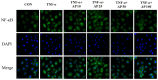
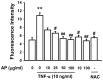
Vascular inflammation plays a key role in the pathogenesis and progression of atherosclerosis, a main complication of diabetes. The present study investigated whether an aqueous extract of Portulaca oleracea (AP) prevents the TNF-α-induced vascular inflammatory process in the human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC). The stimulation of TNF-α induced overexpression of adhesion molecules affects vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1, intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and E-selectin for example. However, AP significantly suppressed TNF-α-induced over-expression of these adhesion molecules in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, pretreatment with AP dose-dependently reduced an increase of the adhesion of HL-60 cells to TNF-α-induced HUVEC. Furthermore, we observed that stimulation of TNF-α significantly increased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. However, pretreatment with AP markedly blocked TNF-α-induced ROS production in a dose-dependent manner. The western blot and immunofluorescence analysis showed that AP inhibited the translocation of p65 NF-κB to the nucleus. In addition, AP suppressed the TNF-α-induced degradation of IκB-α and attenuated the TNF-α-induced NF-κB binding. AP also effectively reduced TNF-α-induced mRNA expressions of monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 and interleukin (IL)-8 in a dose-dependent manner. Taken together, AP prevents the vascular inflammatory process through the inhibition of intracellular ROS production and NF-κB activation as well as the reduction of adhesion molecule expression in TNF-α-induced HUVEC. These results suggested that AP might have a potential therapeutic effect by inhibiting the vascular inflammation process in vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis.
Keywords: NF-κB; Portulaca oleracea; atherosclerosis; inflammation; reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Figures
References
-
- Libby P., Sukhova G., Lee R.T., Galis Z.S. Cytokines regulate vascular functions related to stability of the atherosclerotic plaque. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1995;2:9–12. - PubMed
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis: An inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999;340:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Quagliaro L., Piconi L., Assaloni R., da Ros R., Maier A., Zuodar G., Ceriello A. Intermittent HG enhances ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in culture: The distinct role of protein kinase C and mitochondrial superoxide production. Atherosclerosis. 2005;183:259–267. - PubMed
-
- Minami T., Aird W.C. Endothelial cell gene regulation. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2005;15:174–184. - PubMed
-
- Madge L.A., Pober J.S. TNF signaling in vascular endothelial cells. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2001;70:317–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

