Combinatorial signal integration by APETALA2/Ethylene Response Factor (ERF)-transcription factors and the involvement of AP2-2 in starvation response
- PMID: 22754341
- PMCID: PMC3382747
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms13055933
Combinatorial signal integration by APETALA2/Ethylene Response Factor (ERF)-transcription factors and the involvement of AP2-2 in starvation response
Abstract
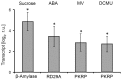
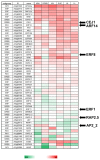
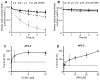
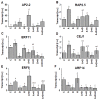
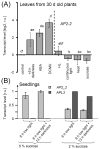
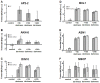
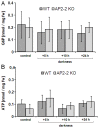
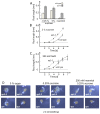
Transcription factors of the APETALA 2/Ethylene Response Factor (AP2/ERF)- family have been implicated in diverse processes during development, stress acclimation and retrograde signaling. Fifty-three leaf-expressed AP2/ERFs were screened for their transcriptional response to abscisic acid (ABA), 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea (DCMU), methylviologen (MV), sucrose and high or low light, respectively, and revealed high reactivity to these effectors. Six of them (AP2-2, ARF14, CEJ1, ERF8, ERF11, RAP2.5) were selected for combinatorial response analysis to ABA, DCMU and high light. Additive, synergistic and antagonistic effects demonstrated that these transcription factors are components of multiple signaling pathways. AP2-2 (At1g79700) was subjected to an in depth study. AP2-2 transcripts were high under conditions linked to limited carbohydrate availability and stress and down-regulated in extended light phase, high light or in the presence of sugar. ap2-2 knock out plants had unchanged metabolite profiles and transcript levels of co-expressed genes in extended darkness. However, ap2-2 revealed more efficient germination and faster early growth under high sugar, osmotic or salinity stress, but the difference was abolished in the absence of sugar or during subsequent growth. It is suggested that AP2-2 is involved in mediating starvation-related and hormonal signals.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; abscisic acid; apetala2/ethylene response factor; germination; photosynthesis; retrograde signaling; transcription factor.
Figures
References
-
- Riechmann J.L., Heard J., Martin G., Reuber L., Jiang C.Z., Keddie J., Adam L., Pineda O., Ratcliffe O.J., Samaha R.R., et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science. 2000;290:2105–2110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

