Adsorption of Cr(VI) and speciation of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) in aqueous solutions using chemically modified chitosan
- PMID: 22754471
- PMCID: PMC3386586
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph9051757
Adsorption of Cr(VI) and speciation of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) in aqueous solutions using chemically modified chitosan
Abstract
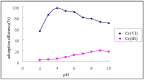
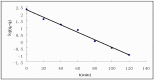
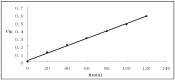
A new type of grafting chitosan (CTS) was synthesized using 2-hydroxyethyl-trimethyl ammonium chloride (HGCTS). The adsorption of Cr(VI) on HGCTS was studied. The effect factors on adsorption and the adsorption mechanism were considered. The results indicated that the HGCTS could concentrate and separate Cr(VI) at pH 4.0; the adsorption equilibrium time was 80 min; the maximum adsorption capacity was 205 mg/g. The adsorption isotherm and kinetics were investigated, equilibrium data agreed very well with the Langmuir model and the pseudo second-order model could describe the adsorption process better than the pseudo first-order model. A novel method for speciation of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) in environmental water samples has been developed using HGCTS as adsorbent and FAAS as determination means. The detection limit of this method was 20 ng/L, the relatively standard deviation was 1.2% and the recovery was 99%~105%.
Keywords: chromium; flame atomic absorption spectrometry; grafting chitosan; speciation.
Figures
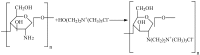

References
-
- Kot A., Namiesnik J. The role of speciation in analytical chemistry. Trends Anal.Chem. 2000;19:69–79. doi: 10.1016/S0165-9936(99)00195-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

