In vivo assessment of osseous wound healing using a novel bone putty containing lidocaine in the surgical management of tooth extractions
- PMID: 22754572
- PMCID: PMC3382256
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/894815
In vivo assessment of osseous wound healing using a novel bone putty containing lidocaine in the surgical management of tooth extractions
Abstract
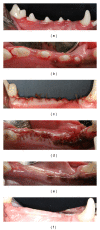
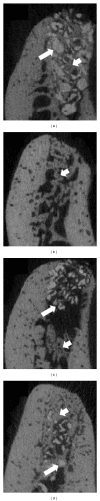
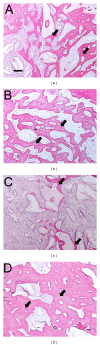
Objective. This preclinical pilot study evaluated the systemic, radiographic, and histological responses to bone putty containing lidocaine in a canine tooth extraction model. Methods. In five beagle dogs the right mandibular premolars were extracted and sockets grafted with (1) xenograft particulate bone and a collagen sponge plug (control), (2) bone putty alone, (3) bone putty mixed with xenograft (3 : 1), or (4) xenograft sandwiched between bone putty. At 6 weeks post-op, the systemic and local responses were evaluated using a blood chemistry panel, micro-CT, and histological analyses. Results. No significant differences in blood chemistries were noted at 6 weeks postgrafting compared to baseline. Sockets grafted with either bone putty formulation demonstrated comparable radiographic and histologic evidence of bone healing compared to control sockets. Conclusions. Our preclinical results indicate that this bone putty appears to be a safe biocompatible device that may be useful in the postoperative management of tooth extractions.
Figures


References
-
- Malamed SF. Local anesthetics: dentistry’s most important drugs, clinical update 2006. Journal of the California Dental Association. 2006;34(12):971–976. - PubMed
-
- Bouloux GF, Steed MB, Perciaccante VJ. Complications of third molar surgery. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America. 2007;19(1):117–128. - PubMed
-
- Scully C. Medical Problems in Dentistry. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010. Haematology; pp. 177–233.
-
- Seymour AR, Meechan JG, Yates SM. Pharmacology and Dental Therapeutics. New York, NY, USA: Oxford University Press; 1999. Aspirin, other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and paracetamol; pp. 89–94.
-
- Fischer LM, Schlienger RG, Matter CM, Jick H, Meier CR. Discontinuation of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy and risk of acute myocardial infarction. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2004;164(22):2472–2476. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

