Transplanted bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve memory in rat models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22754576
- PMCID: PMC3382392
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/369417
Transplanted bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve memory in rat models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
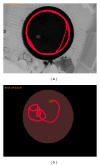
The present study aims to evaluate the effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) grafts on cognition deficit in chemically and age-induced Alzheimer's models of rats. In the first experiments aged animals (30 months) were tested in Morris water maze (MWM) and divided into two groups: impaired memory and unimpaired memory. Impaired groups were divided into two groups and cannulated bilaterally at the CA1 of the hippocampus for delivery of mesenchymal stem cells (500 × 10(3)/μL) and PBS (phosphate buffer saline). In the second experiment, Ibotenic acid (Ibo) was injected bilaterally into the nucleus basalis magnocellularis (NBM) of young rats (3 months) and animals were tested in MWM. Then, animals with memory impairment received the following treatments: MSCs (500 × 10(3)/μL) and PBS. Two months after the treatments, cognitive recovery was assessed by MWM in relearning paradigm in both experiments. Results showed that MSCs treatment significantly increased learning ability and memory in both age- and Ibo-induced memory impairment. Adult bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells show promise in treating cognitive decline associated with aging and NBM lesions.
Figures

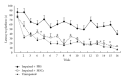

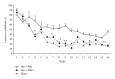
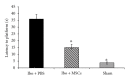
References
-
- Alcyr A, Oliveira JR, Hodges HM. Alzheimer’s disease and neural transplantation as prospective cell therapy. Current Alzheimer Research. 2005;2(1):79–95. - PubMed
-
- Marin DB, Sewell MC, Schlechter A. Alzheimer’s disease: accurate and early diagnosis in the primary care setting. Geriatrics. 2002;57(2):36–40. - PubMed
-
- Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, et al. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Annals of Neurology. 1991;30(4):572–580. - PubMed
-
- Jeffrey L, Cummings MD. Cognitive and behavioral heterogeneity in Alzheimer’s disease: seeking the neurobiological basis. Neurobiology of Aging. 2000;21(6):845–861. - PubMed
-
- Crook TH, T. Bartus R, H. Ferris S. Age-associated memory impairment. Developmental Neuropsychology. 1986;2:261–276.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

