Staging a recovery from mitotic arrest: Unusual ways of Cdk1
- PMID: 22754627
- PMCID: PMC3383719
- DOI: 10.4161/bioa.20421
Staging a recovery from mitotic arrest: Unusual ways of Cdk1
Abstract
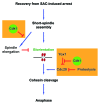
Checkpoint controls, the surveillance pathways that impose "an order of execution" on the major cell cycle events, are critical to the maintenance of genome stability. When cells fail to execute a cellular event or do so erroneously due to misregulation or exposure to genotoxic stresses, these evolutionarily conserved regulatory circuits prevent passage to the subsequent event, thus bringing the cell cycle to a halt. Once the checkpoint stimulus is removed, cells recover from the arrest and eventually resume cell cycle progression. While the activation, execution and maintenance, the three major aspects of the checkpoint controls, have been investigated in detail, the recovery process remains underexplored. It is not clear if cells recover passively upon dissipation of the checkpoint signals or require an active participation by specific effectors. A recent study in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae uncovered two previously unsuspected functions of Cdk1 in efficient recovery from the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) imposed arrest. An inability to fulfil these requirements in the absence of Cdk1 makes it virtually impossible for cells to recover from the mitotic arrest. Given the conserved nature of the SAC, these findings may have implications for vertebrate cells.
Figures
Comment in
- Liang H, Lim HH, Venkitaraman A, Surana U. Cdk1 promotes kinetochore bi-orientation and regulates Cdc20 expression during recovery from spindle checkpoint arrest. EMBO J. 2012;31:403–16. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.385.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
