Authentication of the R06E fruit bat cell line
- PMID: 22754654
- PMCID: PMC3386627
- DOI: 10.3390/v4050889
Authentication of the R06E fruit bat cell line
Abstract
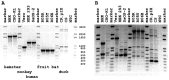
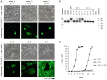
Fruit bats and insectivorous bats are believed to provide a natural reservoir for a wide variety of infectious diseases. Several lines of evidence, including the successful isolation of infectious viruses, indicate that Marburg virus and Ravn virus have found a major reservoir in colonies of the Egyptian rousette (Rousettus aegyptiacus). To facilitate molecular studies on virus-reservoir host interactions and isolation of viruses from environmental samples, we established cell lines from primary cells of this animal. The cell lines were given to several laboratories until we realized that a contamination with Vero cells in one of the cultures had occurred. Here we describe a general diagnostic procedure for identification of cross-species contamination with the focus on Vero and Rousettus cell lines, and summarize newly discovered properties of the cell lines that may pertain to pathogen discovery.
Keywords: R05T; R06E; Rousettus aegyptiacus; fruit bat cell line.
Figures

References
-
- Leroy E.M., Kumulungui B., Pourrut X., Rouquet P., Hassanin A., Yaba P., Delicat A., Paweska J.T., Gonzalez J.P., Swanepoel R. Fruit bats as reservoirs of Ebola virus. Nature. 2005;438:575–576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

