The overlooked greatwall: a new perspective on mitotic control
- PMID: 22754657
- PMCID: PMC3382961
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.120023
The overlooked greatwall: a new perspective on mitotic control
Abstract
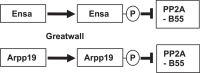
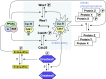
The role of the dual specificity protein phosphatase, Cdc25, in activating the cyclin-dependent kinase-cyclin B complex (Cdk1-CycB) by overcoming the inhibitory Wee1 kinase is a long-established principle for mitotic entry. Recently, however, evidence has emerged of a regulatory network that facilitates Cdk1-CycB activity by inhibiting the form of protein phosphatase 2A having a B55 regulatory subunit (PP2A-B55). Here, I review the genetic and biochemical evidence for Greatwall kinase and its substrate Endosulphine as the key components of this previously obscure regulatory network. Not only is the inhibition of PP2A-B55 by phospho-endosulphine required to prevent dephosphorylation of Cdk1-CycB substrates until mitotic exit, but it is also required to promote Cdc25 activity and inhibit Wee1 at mitotic entry. I discuss how these alternating states of preferential PP2A-B55 or Cdk1-CycB activity can have an impact upon the regulation of Polo kinase and its ability to bind different partner proteins as mitosis progresses.
Keywords: Endos; Greatwall kinase; PP2A; mitosis.
Figures

References
-
- Masui Y, Markert CL. 1971. Cytoplasmic control of nuclear behavior during meiotic maturation of frog oocytes. J. Exp. Zool. 177, 129–145 10.1002/jez.1401770202 (doi:10.1002/jez.1401770202) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reynhout JK, Smith LD. 1974. Studies on the appearance and nature of a maturation-inducing factor in the cytoplasm of amphibian oocytes exposed to progesterone. Dev. Biol. 38, 394–400 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90016-5 (doi:10.1016/0012-1606(74)90016-5) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kishimoto T, Kanatani H. 1976. Cytoplasmic factor responsible for germinal vesicle breakdown and meiotic maturation in starfish oocyte. Nature 260, 321–322 10.1038/260321a0 (doi:10.1038/260321a0) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guerrier P, Doree M, Freyssimet G. 1975. Early stimulation of protein kinase activity during hormonal meiosis reinitiation in starfish ovocytes. C R. Acad. Sci. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci. D. 281, 1475–1478 - PubMed
-
- Lohka M, Masui Y. 1983. Formation in vitro of sperm pronuclei and mitotic chromosomes induced by amphibian ooplasmic components. Science 220, 719–721 10.1126/science.6601299 (doi:10.1126/science.6601299) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
