Management of massive soft tissue defects: The use of INTEGRA® artificial skin after necrotizing soft tissue infection of the chest
- PMID: 22754676
- PMCID: PMC3378193
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2012.05.12
Management of massive soft tissue defects: The use of INTEGRA® artificial skin after necrotizing soft tissue infection of the chest
Abstract
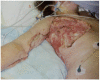
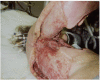
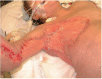
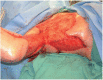
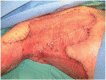
Necrotizing soft tissue infection, such as necrotizing fasciitis, is a group of highly lethal infections especially when the chest is involved due to increased risk of pulmonary complications. Because aggressive radical debridement of all poorly perfused tissue is required, patients frequently suffer from massive skin defects, which often requires autograft skin grafting or myocutaneous flaps. However, options are limited in patients with limited autograft donor availability, or questionable underlying wound bed viability, such as in scleroderma. Here, we report the case of a 49 year old female with scleroderma who suffered from a necrotizing soft tissue infection of the chest extending to her right upper arm, underwent multiple radical debridements, and reconstruction of the consequent massive chest wall defect with INTEGRA® bilaminar dermal regeneration template. This approach required a thinner skin graft without flaps, allowed for the inherently diseased donor site to heal adequately, and avoided major infections and wound complications. This report highlights an important management option for this challenging disease.
Keywords: Chest necrotizing fasciitis; Integra.
Figures
References
-
- Drake DB, Woods JA, Bill TJ, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in the early diagnosis of group A beta streptococcal necrotizing fasciitis: a case report. J Emerg Med. 1998;16:403-407 - PubMed
-
- Edlich RF, Winters KL, Woodard CR, et al. Massive soft tissue infections: necrotizing fasciitis and purpura fulminans. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2005;15:57-65 - PubMed
-
- Urschel JD, Takita H, Antkowiak JG. Necrotizing soft tissue infections of the chest wall. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997;64:276-279 - PubMed
-
- Cohen M, Ramasastry SS. Reconstruction of complex chest wall defects. Am J Surg. 1996;172:35-40 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
