The role of transesophageal echocardiography in the intraoperative period
- PMID: 22758616
- PMCID: PMC3263482
- DOI: 10.2174/157340311798220511
The role of transesophageal echocardiography in the intraoperative period
Abstract
The goal of hemodynamic monitoring and management during major surgery is to guarantee adequate organ perfusion, a major prerequisite for adequate tissue oxygenation and thus, end-organ function. Further, hemodynamic monitoring should serve to prevent, detect, and to effectively guide treatment of potentially life-threatening hemodynamic events, such as severe hypovolemia due to hemorrhage, or cardiac failure. The ideal monitoring device does not exist, but some conditions must be met: it should be easy and operator-independently to use; it should provide adequate, reproducible information in real time. In this review we discuss in particular the role of intraoperative use of transesophageal echocardiography (TOE). Although TOE has gained special relevance in cardiac surgery, its role in major non cardiac surgery is still to be determined. We particularly focus on its ability to provide measurements of cardiac output (CO), and its role to guide fluid therapy. Within the last decade, concepts oriented on optimizing stroke volume and cardiac output mainly by fluid administration and guided by continuous monitoring of cardiac output or so called functional parameters of cardiac preload gained particular attention. Although they are potentially linked to an increased amount of fluid infusion, recent data give evidence that such pre-emptive concepts of hemodynamic optimization result in a decrease in morbidity and mortality. As TOE allows a real time direct visualization of cardiac structures, other potentially important advantages of its use also outside the cardiac surgery operation room can be postulated, namely the ability to evaluate the anatomical and functional integrity of the left and the right heart chambers. Finally, a practical approach to TOE monitoring is presented, based on a local experience.
Figures
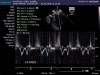
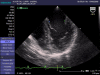
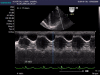
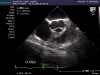
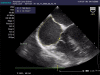
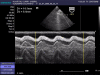
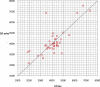

Similar articles
-
[The role of transesophageal echocardiography in intraoperative hemodynamic monitoring].Minerva Anestesiol. 2001 Apr;67(4):320-4. Minerva Anestesiol. 2001. PMID: 11376533 Italian.
-
[A Chinese consensus statement on the clinical application of transesophageal echocardiography for critical care (2019)].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Dec 1;58(12):869-882. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2019.12.002. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31775449 Chinese.
-
Volumetric preload measurement by thermodilution: a comparison with transoesophageal echocardiography.Br J Anaesth. 2005 Jun;94(6):748-55. doi: 10.1093/bja/aei123. Epub 2005 Mar 24. Br J Anaesth. 2005. PMID: 15790674
-
Is There a Need for a Pulmonary Artery Catheter in Cardiac Surgery Today?Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2021 Mar;25(1):29-33. doi: 10.1177/1089253220951322. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2021. PMID: 32847478 Review.
-
Transoesophageal echocardiography (TOE) in the operating room.Br J Anaesth. 2006 Jul;97(1):77-84. doi: 10.1093/bja/ael122. Epub 2006 Jun 1. Br J Anaesth. 2006. PMID: 16740605 Review.
Cited by
-
An Approach to Anesthetic Management of Venous Anomalies and Outflow Reconstruction in Liver Transplants.Cureus. 2023 Aug 24;15(8):e44059. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44059. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37746456 Free PMC article.
-
Management of acute intra-operative thromboembolism in renal cell carcinoma.Anesth Essays Res. 2015 Sep-Dec;9(3):417-9. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.158011. Anesth Essays Res. 2015. PMID: 26712987 Free PMC article.
-
Stunned Myocardium as a Sequela of Acute Severe Anemia: An Adult Simulation Case for Anesthesiology Residents.MedEdPORTAL. 2024 Sep 6;20:11432. doi: 10.15766/mep_2374-8265.11432. eCollection 2024. MedEdPORTAL. 2024. PMID: 39247162 Free PMC article.
-
The Lifelong Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Clinical Prediction Models on Patients With Tetralogy of Fallot.CJC Pediatr Congenit Heart Dis. 2023 Aug 29;2(6Part A):440-452. doi: 10.1016/j.cjcpc.2023.08.005. eCollection 2023 Dec. CJC Pediatr Congenit Heart Dis. 2023. PMID: 38161675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular manifestation of end-stage liver disease and perioperative echocardiography for liver transplantation: anesthesiologist's view.Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2022 Apr;17(2):132-144. doi: 10.17085/apm.22132. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2022. PMID: 35538654 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Connors AF, Jr, Speroff T, Dawson NV, et al. The effectiveness of right heart catheterization in the initial care of critically ill patients. SUPPORT Investigators. JAMA. 1996;276(11):889–97. - PubMed
-
- Sandham JD, Hull RD, Brant RF, et al. Canadian Critical Care Clinical Trials Group. A randomized, controlled trial of the use of pulmonary-artery catheters in high-risk surgical patients. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(1):5–14. - PubMed
-
- Oxorn D. Non-invasive imaging. Intraoperative echocardiography. Heart. 2008;94:1236–43. - PubMed
-
- Minhaj M, Patel K, Muzic D, et al. The effect of intraopeative trasesophageal echocardiography on surgical management. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2007;21:800–4. - PubMed
-
- Kovlev N, Brase R, Swanevelder J, et al. The influence of trnasesophageal echocardiography on intraoperative decision making. A European multicentre study. Anaesthesia. 1998;53:767–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

