Alveolar macrophage cathelicidin deficiency in severe sarcoidosis
- PMID: 22759465
- PMCID: PMC3472801
- DOI: 10.1159/000339149
Alveolar macrophage cathelicidin deficiency in severe sarcoidosis
Abstract
Background: Dysfunctional immune responses characterize sarcoidosis, but the status of cathelicidin, a potent immunoregulatory and antimicrobial molecule, has not been established in clinical disease activity.
Methods: Alveolar macrophage cathelicidin expression was determined in biopsy-proven sarcoidosis patients classified clinically as 'severe' (requiring systemic treatment) or 'non-severe' (never requiring treatment). Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells from sarcoidosis patients and healthy controls were analyzed for mRNA expression of cathelicidin, vitamin D receptor (VDR) and the VDR coactivator steroid receptor coactivator-3 (SRC3) by quantitative PCR. Cathelicidin-derived peptide LL-37 was determined by immunocytochemistry. Serum calcidiol (25-hydroxyvitamin D2; vitD2) and calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3; vitD3) were quantified.
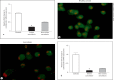
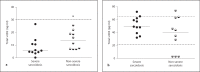
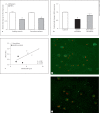
Results: The results indicated reduced BAL cell expression of cathelicidin and SRC3 in severe but not non-severe sarcoidosis compared to controls. Serum levels of biologically active vitD3 in both severe and non-severe patients were within the control range even though vitD2 levels in both groups were below the recommended level (30 ng/ml). Sarcoidosis and control alveolar macrophages were studied in vitro to determine cathelicidin responses to vitD3 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), a vitD3 antagonist elevated in active sarcoidosis. Alveolar macrophage cathelicidin was stimulated by vitD3 but repressed by TNFα, which also repressed SRC3.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that TNFα-mediated repression of SRC3 contributes to alveolar macrophage cathelicidin deficiency in severe sarcoidosis despite healthy vitD3 levels. Deficiency of cathelicidin, a multifunctional regulator of immune cells and proinflammatory cytokines, may impede resolution of inflammation in the lungs of patients with severe sarcoidosis.
Copyright © 2012 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

References
-
- Chen ES, Moller DR. Sarcoidosis - scientific progress and clinical challenges. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7:457–467. - PubMed
-
- Iannuzzi MC, Rybicki BA, Teirstein AS. Sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2153–2165. - PubMed
-
- Opitz B, van Laak V, Eitel J, Suttorp N. Innate immune recognition in infectious and noninfectious diseases of the lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181:1294–1309. - PubMed
-
- Nijnik A, Hancock RE. The roles of cathelicidin LL-37 in immune defences and novel clinical applications. Curr Opin Hematol. 2009;16:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Sorensen OE, Follin P, Johnsen AH, Calafat J, Tjabringa GS, Hiemstra PS, Borregaard N. Human cathelicidin, hCAP-18, is processed to the antimicrobial peptide LL-37 by extracellular cleavage with proteinase 3. Blood. 2001;97:3951–3959. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

