Identification and characterization of resistance to cowpea aphid (Aphis craccivora Koch) in Medicago truncatula
- PMID: 22759788
- PMCID: PMC3464659
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-101
Identification and characterization of resistance to cowpea aphid (Aphis craccivora Koch) in Medicago truncatula
Abstract
Background: Cowpea aphid (CPA; Aphis craccivora) is the most important insect pest of cowpea and also causes significant yield losses in other legume crops including alfalfa, beans, chickpea, lentils, lupins and peanuts. In many of these crops there is no natural genetic resistance to this sap-sucking insect or resistance genes have been overcome by newly emerged CPA biotypes.
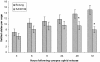
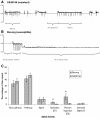
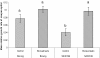
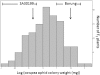
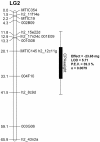
Results: In this study, we screened a subset of the Medicago truncatula core collection of the South Australian Research and Development Institute (SARDI) and identified strong resistance to CPA in a M. truncatula accession SA30199, compared to all other M. truncatula accessions tested. The biology of resistance to CPA in SA30199 plants was characterised compared to the highly susceptible accession Borung and showed that resistance occurred at the level of the phloem, required an intact plant and involved a combination of antixenosis and antibiosis. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis using a F2 population (n = 150) from a cross between SA30199 and Borung revealed that resistance to CPA is controlled in part by a major quantitative trait locus (QTL) on chromosome 2, explaining 39% of the antibiosis resistance.
Conclusions: The identification of strong CPA resistance in M. truncatula allows for the identification of key regulators and genes important in this model legume to give effective CPA resistance that may have relevance for other legume crops. The identified locus will also facilitate marker assisted breeding of M. truncatula for increased resistance to CPA and potentially other closely related Medicago species such as alfalfa.
Figures
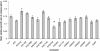

Similar articles
-
Characterization and genetic dissection of resistance to spotted alfalfa aphid (Therioaphis trifolii) in Medicago truncatula.J Exp Bot. 2013 Nov;64(16):5157-72. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert305. Epub 2013 Sep 21. J Exp Bot. 2013. PMID: 24058162 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of distinct quantitative trait loci associated with defence against the closely related aphids Acyrthosiphon pisum and A. kondoi in Medicago truncatula.J Exp Bot. 2012 Jun;63(10):3913-22. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers084. Epub 2012 Mar 21. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 22442407 Free PMC article.
-
Aphid resistance in Medicago truncatula involves antixenosis and phloem-specific, inducible antibiosis, and maps to a single locus flanked by NBS-LRR resistance gene analogs.Plant Physiol. 2005 Apr;137(4):1445-55. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.051243. Epub 2005 Mar 18. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15778464 Free PMC article.
-
Annual Medicago: from a model crop challenged by a spectrum of necrotrophic pathogens to a model plant to explore the nature of disease resistance.Ann Bot. 2006 Dec;98(6):1117-28. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcl132. Epub 2006 Jun 27. Ann Bot. 2006. PMID: 16803846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genetic Control of the Compound Leaf Patterning in Medicago truncatula.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jan 13;12:749989. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.749989. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35095943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Mapping of a Major Resistance Gene to Pea Aphid (Acyrthosipon pisum) in the Model Legume Medicago truncatula.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 29;17(8):1224. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081224. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27483247 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships Between Aphids (Insecta: Homoptera: Aphididae) and Slugs (Gastropoda: Stylommatophora: Agriolimacidae) Pests of Legumes (Fabaceae: Lupinus).J Insect Sci. 2016 Jun 20;16(1):52. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/iew033. Print 2016. J Insect Sci. 2016. PMID: 27324580 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress and Prospect of Alfalfa Resistance to Pathogens and Pests.Plants (Basel). 2022 Aug 1;11(15):2008. doi: 10.3390/plants11152008. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35956485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial distribution and community structure of microbiota associated with cowpea aphid (Aphis craccivora Koch).3 Biotech. 2022 Mar;12(3):75. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03142-1. Epub 2022 Feb 21. 3 Biotech. 2022. PMID: 35251878 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and genetic dissection of resistance to spotted alfalfa aphid (Therioaphis trifolii) in Medicago truncatula.J Exp Bot. 2013 Nov;64(16):5157-72. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert305. Epub 2013 Sep 21. J Exp Bot. 2013. PMID: 24058162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dixon AFG. Aphid ecology: an optimization approach. 2. Chapman and Hall, London; 1998.
-
- Blackman RL, Eastop VF. Aphids on the world's crops: an identification and information guide. John Wiley & Sons, Chichister; 2000.
-
- Couldridge C, Newbury HJ, Ford-Lloyd B, Bale J, Pritchard J. Exploring plant responses to aphid feeding using a full Arabidopsis microarray reveals a small number of genes with significantly altered expression. Bull Entomol Res. 2007;97:523–532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

