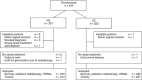
Vinorelbine and gemcitabine vs vinorelbine and carboplatin as first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC. A phase III randomised controlled trial by the Norwegian Lung Cancer Study Group
- PMID: 22759880
- PMCID: PMC3405221
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.284
Vinorelbine and gemcitabine vs vinorelbine and carboplatin as first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC. A phase III randomised controlled trial by the Norwegian Lung Cancer Study Group
Abstract
Background: Platinum-based doublet chemotherapy is the standard first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but earlier studies have suggested that non-platinum combinations are equally effective and better tolerated. We conducted a national, randomised study to compare a non-platinum with a platinum combination.
Methods: Eligible patients had stage IIIB/IV NSCLC and performance status (PS) 0-2. Patients received up to three cycles of vinorelbine 60 mg m(-2) p.o.+gemcitabine 1000 mg m(-2) i.v. day 1 and 8 (VG) or vinorelbine 60 mg m(-2) p.o. day 1 and 8+carboplatin area under the curve=5 (Calvert's formula) i.v. day 1 (VC). Patients ≥75 years received 75% of the dose. Endpoints were overall survival, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), toxicity, and the use of radiotherapy.
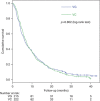
Results: We randomised 444 patients from September 2007 to April 2009. The median age was 65 years, 58% were men and 25% had PS 2. Median survival was VG: 6.3 months; VC: 7.0 months, P=0.802. Vinorelbine plus carboplatin patients had more grade III/IV nausea/vomiting (VG: 4%, VC: 12%, P=0.008) and grade IV neutropenia (VG: 7%, VC: 19%, P<0.001). Infections, HRQoL and the use of radiotherapy did not differ significantly between the treatment groups.
Conclusion: The two regimens yielded similar overall survival. The VG combination had only a slightly better toxicity profile.
© 2012 Cancer Research UK
Figures
References
-
- Aapro M, Finek J (2011) Oral vinorelbine in metastatic breast cancer: A review of current clinical trial results. Cancer Treat Rev 38(2): 120–126 - PubMed
-
- Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, Filiberti A, Flechtner H, Fleishman SB, de Haes JC (1993) The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst 85: 365–376 - PubMed
-
- Azzoli CG, Baker Jr S, Temin S, Pao W, Aliff T, Brahmer J, Johnson DH, Laskin JL, Masters G, Milton D, Nordquist L, Pfister DG, Piantadosi S, Schiller JH, Smith R, Smith TJ, Strawn JR, Trent D, Giaccone G (2009) American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline update on chemotherapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 27: 6251–6266 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azzoli CG, Temin S, Aliff T, Baker Jr S, Brahmer J, Johnson DH, Laskin JL, Masters G, Milton D, Nordquist L, Pao W, Pfister DG, Piantadosi S, Schiller JH, Smith R, Smith TJ, Strawn JR, Trent D, Giaccone G (2011) 2011 Focused Update of 2009 American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update on Chemotherapy for Stage IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J Clin Oncol 29: 3825–3831 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barlesi F, Pujol JL (2005) Combination of chemotherapy without platinum compounds in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review of phase III trials. Lung Cancer 49: 289–298 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous