Metabolic profiling of Lactococcus lactis under different culture conditions
- PMID: 22759915
- PMCID: PMC6268593
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17078022
Metabolic profiling of Lactococcus lactis under different culture conditions
Abstract
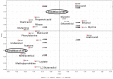
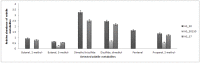
Gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and headspace gas chromatography mass spectrometry (HS/GC-MS) were used to study metabolites produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris MG1363 grown at a temperature of 30 °C with and without agitation at 150 rpm, and at 37 °C without agitation. It was observed that L. lactis produced more organic acids under agitation. Primary alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and polyols were identified as the corresponding trimethylsilyl (TMS) derivatives, whereas amino acids and organic acids, including fatty acids, were detected through methyl chloroformate derivatization. HS analysis indicated that branched-chain methyl aldehydes, including 2-methylbutanal, 3-methylbutanal, and 2-methylpropanal are degdradation products of isoleucine, leucine or valine. Multivariate analysis (MVA) using partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) revealed the major differences between treatments were due to changes of amino acids and fermentation products.
Figures




References
-
- Mireille Y., Chistophe G., Emilie C., Gaelle B., Veronique M. The initial efficiency of the proteolytic systems of Lactococcus lactis strains determines their responses to a cheese environment. Int. Dairy J. 2011;21:335–345.
-
- Guimont C. Change of free amino acids in M17 medium after growth of Streptococcus thermophilus and identification of a glutamine transport ATP-binding protein. Int. Dairy J. 2002;12:729–736. doi: 10.1016/S0958-6946(02)00068-7. - DOI
-
- Amel T., Nassra D., Maryse L., Denis R., Gisele L. Comparative transcriptome analysis of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris strains under conditions simulating Cheddar cheese manufacture. 2011;146:263–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

