Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) is a tissue biomarker for detection of early hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis
- PMID: 22760167
- PMCID: PMC3425156
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-5-37
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) is a tissue biomarker for detection of early hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors occurring mainly in patients with chronic liver disease. Detection of early HCC is critically important for treatment of these patients.
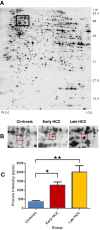
Methods: We employed a proteomic profiling approach to identify potential biomarker for early HCC detection. Based on Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging classification, 15 early HCC and 25 late HCC tissue samples from post-operative HCC patients and their clinicopathological data were used for the discovery of biomarkers specific for the detection of early HCC. Differential proteins among cirrhotic, early, and late tissue samples were separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) and subsequently identified by mass spectrometry (MS). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves analysis were performed to find potential biomarkers associated with early HCC. Diagnosis performance of the biomarker was obtained from diagnosis test.
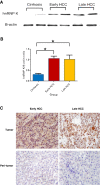
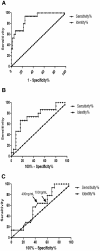
Results: Protein spot SSP2215 was found to be significantly overexpressed in HCC, particularly in early HCC, and identified as heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) by tandem mass spectrometry (MALDI TOF/TOF). The overexpression in HCC was subsequently validated by western blot and immunohistochemistry. ROC curve analysis showed that hnRNP K intensity could detect early HCC at 66.67 % sensitivity and 84 % specificity, which was superior to serum α-fetoprotein (AFP) in detection of early HCC. Furthermore, the diagnosis test demonstrated, when combined with hnRNP K and serum AFP as biomarker panel to detect early HCC at different cut-off value, the sensitivity and specificity could be enhanced to 93.33 % and 96 %, respectively.
Conclusions: hnRNP K is a potential tissue biomarker, either alone or in combination with serum AFP, for detection of early HCC. High expression of hnRNP K could be helpful to discriminate early HCC from a nonmalignant nodule, especially for patients with liver cirrhosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alpha-Fetoprotein Measurement Benefits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance in Patients with Cirrhosis.Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun;110(6):836-44; quiz 845. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2015.100. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25869392
-
Enhanced detection of early hepatocellular carcinoma by serum SELDI-TOF proteomic signature combined with alpha-fetoprotein marker.Ann Surg Oncol. 2010 Sep;17(9):2518-25. doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-1038-8. Epub 2010 Mar 31. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20354800 Free PMC article.
-
PIVKA-II serves as a potential biomarker that complements AFP for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Apr 13;21(1):401. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08138-3. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33849479 Free PMC article.
-
Glycoproteomic markers of hepatocellular carcinoma-mass spectrometry based approaches.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2019 May;38(3):265-290. doi: 10.1002/mas.21583. Epub 2018 Nov 25. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2019. PMID: 30472795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Clin Liver Dis. 2020 Nov;24(4):611-621. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2020.07.013. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Clin Liver Dis. 2020. PMID: 33012448 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiosensitization and downregulation of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) upon inhibition of mitogen/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK) in malignant melanoma cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Jul 10;6(19):17178-91. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3935. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26136337 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC-1 cofactors regulate APOBEC3-induced mutations in hepatitis B virus.J Virol. 2025 Feb 25;99(2):e0187924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01879-24. Epub 2025 Jan 27. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 39868801 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Cyclin D1 and Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein-K (HnRNP-K) on Urinary Bladder Carcinogenesis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Feb 26;19(2):513-519. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.2.513. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 29480994 Free PMC article.
-
PROX1 promotes breast cancer invasion and metastasis through WNT/β-catenin pathway via interacting with hnRNPK.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Feb 28;18(5):2032-2046. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.68960. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35342346 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0062682 Binds to YBX1 and Promotes Oncogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 19;14(18):4524. doi: 10.3390/cancers14184524. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gebo KA, Chander G, Jenckes MW, Ghanem KG, Herlong HF, Torbenson MS, El-Kamary SS, Bass EB. Screening tests for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review. Hepatology. 2002;36:S84–S92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

