Genome-wide identification of Brassica napus microRNAs and their targets in response to cadmium
- PMID: 22760473
- PMCID: PMC3421990
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ers136
Genome-wide identification of Brassica napus microRNAs and their targets in response to cadmium
Abstract
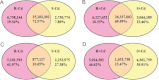
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a distinct class of small RNAs in plants that not only regulate biological processes but also regulate response to environmental stresses. The toxic heavy metal cadmium (Cd) induces expression of several miRNAs in rapeseed (Brassica napus), but it is not known on a genome-wide scale how the expression of miRNAs and their target genes, is regulated by Cd. In this study, four small RNA libraries and four degradome libraries were constructed from Cd-treated and non-Cd-treated roots and shoots of B. napus seedlings. Using high-throughput sequencing, the study identified 84 conserved and non-conserved miRNAs (belonging to 37 miRNA families) from Cd-treated and non-treated B. napus, including 19 miRNA members that were not identified before. Some of the miRNAs were validated by RNA gel blotting. Most of the identified miRNAs were found to be differentially expressed in roots/shoots or regulated by Cd exposure. The study simultaneously identified 802 targets for the 37 (24 conserved and 13 non-conserved) miRNA families, from which there are 200, 537, and 65 targets, belonging to categories I, II, and III, respectively. In category I alone, many novel targets for miRNAs were identified and shown to be involved in plant response to Cd.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad I, Naeem M, Khan N, Samiullah A. 2009. Effects of cadmium stress upon activities of antioxidative enzymes, photosynthetic rate, and production of phytochelatins in leaves and chloroplasts of wheat cultivars differing in yield potential Photosynthetica 47,146 151
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

