Development of a class-specific polyclonal antibody-based indirect competitive ELISA for detecting fluoroquinolone residues in milk
- PMID: 22761246
- PMCID: PMC3390712
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1200001
Development of a class-specific polyclonal antibody-based indirect competitive ELISA for detecting fluoroquinolone residues in milk
Abstract
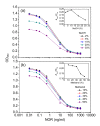
Modified 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) method was employed to synthesize the artificial antigen of norfloxacin (NOR), and New Zealand rabbits were used to produce anti-NOR polyclonal antibody (pAb). Based on the checkerboard titration, an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (icELISA) standard curve was established. This assay was sensitive and had a working range from 0.12 to 68.40 ng/ml, with the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) and limit of detection (LOD) values of 2.7 ng/ml and 0.06 ng/ml, respectively. The produced pAb exhibited high cross-reactivity to fluoroquinolones (FQs) tested, and the IC(50) values to enoxacin, ciprofloxacin, and pefloxacin were 3.1, 3.4, and 4.1 ng/ml, respectively. It also indicated that the concentrations of NaOH and methanol in assay buffer should not be higher than 10% and 30%. When spiked in milk at 5, 20, and 50 ng/ml, the recoveries for NOR, enoxacin, ciprofloxacin, and pefloxacin ranged 90.5%-98.0%, 84.0%-95.2%, 94.0%-106.0%, and 89.5%-100.0%, respectively. The results suggest that this class-specific pAb-based icELISA could be utilized for the primary screening of FQ residues in animal-original products.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Development of an indirect competitive ELISA for simultaneous detection of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2011 Nov;12(11):884-91. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1100076. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2011. PMID: 22042652 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitive immunoassays based on a monoclonal antibody for detection of marbofloxacin in milk.J Dairy Sci. 2020 Sep;103(9):7791-7800. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-18108. Epub 2020 Jul 16. J Dairy Sci. 2020. PMID: 32684479
-
Preparation of high-affinity rabbit monoclonal antibodies for ciprofloxacin and development of an indirect competitive ELISA for residues in milk.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010 Oct;11(10):812-8. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1000055. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010. PMID: 20872990 Free PMC article.
-
Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody against enrofloxacin.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Jan;23(1):69-75. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1201.01017. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23314370
-
Preparation of anti-gatifloxacin antibody and development of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of gatifloxacin residue in milk.J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Aug 22;55(17):6879-84. doi: 10.1021/jf070978g. Epub 2007 Jul 24. J Agric Food Chem. 2007. PMID: 17645343
Cited by
-
Rapid and Simple Determination of Sarafloxacin and Difloxacin in Beef by Capillary Electrophoresis Coupled with Solid-Phase Extraction.J Anal Methods Chem. 2018 Feb 20;2018:1981436. doi: 10.1155/2018/1981436. eCollection 2018. J Anal Methods Chem. 2018. PMID: 29675283 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Mode Quantitative Immunochromatographic Assay for Highly Sensitive On-Site Detection of Ciprofloxacin in Fish Products.Foods. 2025 Mar 25;14(7):1132. doi: 10.3390/foods14071132. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40238245 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic nanoparticle based purification and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using monoclonal antibody against enrofloxacin.J Vet Sci. 2015;16(4):431-7. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2015.16.4.431. J Vet Sci. 2015. PMID: 26040610 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic Use in Livestock and Residues in Food-A Public Health Threat: A Review.Foods. 2022 May 16;11(10):1430. doi: 10.3390/foods11101430. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35627000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation and Directed Evolution of Anti-Ciprofloxacin ScFv for Immunoassay in Animal-Derived Food.Foods. 2021 Aug 20;10(8):1933. doi: 10.3390/foods10081933. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34441715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dufresne G, Fouquet A, Forsyth D, Tittlemier SA. Multiresidue determination of quinolone and fluoroquinolone antibiotics in fish and shrimp by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J AOAC Int. 2007;90(2):604–612. - PubMed
-
- Hassouan MK, Ballesteros O, Zafra A, Vílchez JL, Navalón A. Multiresidue method for simultaneous determination of quinolone antibacterials in pig kidney samples by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr B. 2007;859(2):282–288. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.10.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

