Hepatitis C virus-mediated inhibition of cathepsin S increases invariant-chain expression on hepatocyte surface
- PMID: 22761382
- PMCID: PMC3446550
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00388-12
Hepatitis C virus-mediated inhibition of cathepsin S increases invariant-chain expression on hepatocyte surface
Abstract
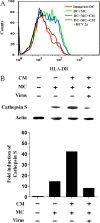
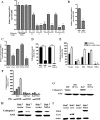
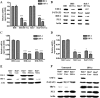
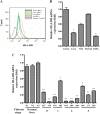
Hepatocytes are the main source of hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication and contain the maximum viral load in an infected person. Chronic HCV infection is characterized by weak cellular immune responses to viral proteins. Cathepsin S is a lysosomal cysteine protease and controls HLA-DR-antigen complex presentation through the degradation of the invariant chain. In this study, we examined the effect of HCV proteins on cathepsin S expression and found it to be markedly decreased in dendritic cells (DCs) exposed to HCV or in hepatocytes expressing HCV proteins. The downregulation of cathepsin S was mediated by HCV core and NS5A proteins involving inhibition of the transcription factors interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) and upstream stimulatory factor 1 (USF-1) in gamma interferon (IFN-γ)-treated hepatocytes. Inhibition of cathepsin S by HCV proteins increased cell surface expression of the invariant chain. In addition, hepatocytes stably transfected with HCV core or NS5A inhibited HLA-DR expression. Together, these results suggested that HCV has an inhibitory role on cathepsin S-mediated major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II maturation, which may contribute to weak immunogenicity of viral antigens in chronically infected humans.
Figures
References
-
- Auffermann-Gretzinger S, Keeffe EB, Levy S. 2001. Impaired dendritic cell maturation in patients with chronic, but not resolved, hepatitis C virus infection. Blood 97:3171–3176 - PubMed
-
- Bain C, et al. 2001. Impaired allostimulatory function of dendritic cells in chronic hepatitis C infection. Gastroenterology 120:512–524 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

