Virion-associated complement regulator CD55 is more potent than CD46 in mediating resistance of mumps virus and vesicular stomatitis virus to neutralization
- PMID: 22761385
- PMCID: PMC3446622
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01154-12
Virion-associated complement regulator CD55 is more potent than CD46 in mediating resistance of mumps virus and vesicular stomatitis virus to neutralization
Abstract
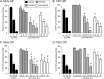
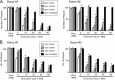
Enveloped viruses can incorporate host cell membrane proteins during the budding process. Here we demonstrate that mumps virus (MuV) and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) assemble to include CD46 and CD55, two host cell regulators which inhibit propagation of complement pathways through distinct mechanisms. Using viruses which incorporated CD46 alone, CD55 alone, or both CD46 and CD55, we have tested the relative contribution of these regulators in resistance to complement-mediated neutralization. Virion-associated CD46 and CD55 were biologically active, with VSV showing higher levels of activity of both cofactors, which promoted factor I-mediated cleavage of C3b into iC3b as well as decay-accelerating factor (DAF) activity against the C3 convertase, than MuV. Time courses of in vitro neutralization with normal human serum (NHS) showed that both regulators could delay neutralization, but viruses containing CD46 alone were neutralized faster and more completely than viruses containing CD55 alone. A dominant inhibitory role for CD55 was most evident for VSV, where virus containing CD55 alone was not substantially different in neutralization kinetics from virus harboring both regulators. Electron microscopy showed that VSV neutralization proceeded through virion aggregation followed by lysis, with virion-associated CD55 providing a delay in both aggregation and lysis more substantial than that conferred by CD46. Our results demonstrate the functional significance of incorporation of host cell factors during virion envelope assembly. They also define pathways of virus complement-mediated neutralization and suggest the design of more effective viral vectors.
Figures


References
-
- Atkinson JP, Liszewski MK, Richards A, Kavanagh D, Moulton EA. 2005. Hemolytic uremic syndrome: an example of insufficient complement regulation on self tissue. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1056:144–152 - PubMed
-
- Beebe DP, Cooper NR. 1981. Neutralization of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) by human complement requires a natural IgM antibody present in human serum. J. Immunol. 126:1562–1568 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

