Sequestosome 1/p62, a scaffolding protein, is a newly identified partner of IRS-1 protein
- PMID: 22761437
- PMCID: PMC3436154
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.322404
Sequestosome 1/p62, a scaffolding protein, is a newly identified partner of IRS-1 protein
Abstract
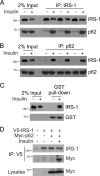
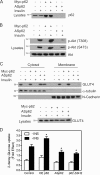
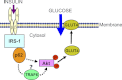
Defects in the insulin-signaling pathway may lead to the development of skeletal muscle insulin resistance, which is one of the earliest abnormalities detected in individuals with the metabolic syndrome and predisposes them to develop type 2 diabetes. Previous studies have shown that deletion of the mouse sequestosome 1/p62 gene results in mature-onset obesity that progresses to insulin and leptin resistance and, ultimately, type 2 diabetes. Sequestosome 1/p62 is involved in receptor-mediated signal transduction and functions as an intracellular signal modulator or adaptor protein. Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) plays a central role in transducing the insulin signal via phosphorylation, protein-protein interactions, and protein modifications. Mapping studies demonstrated that the SH(2) domain at the amino terminus of sequestosome 1/p62 interacts with IRS-1 upon insulin stimulation. Further, IRS-1 interacts with p62 through its YMXM motifs at Tyr-608, Tyr-628, and/or Tyr-658 in a manner similar to its interaction with p85 of phosphoinositol 3-kinase. Overexpression of p62 increased phosphorylation of Akt, GLUT4 translocation, and glucose uptake, providing evidence that p62 participates in the insulin-signaling pathway through its interactions with IRS-1.
Figures


References
-
- Bouzakri K., Koistinen H. A., Zierath J. R. (2005) Molecular mechanisms of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 1, 167–174 - PubMed
-
- Lee J., Pilch P. F., Shoelson S. E., Scarlata S. F. (1997) Conformational changes of the insulin receptor upon insulin binding and activation as monitored by fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry 36, 2701–2708 - PubMed
-
- Myers M. G., Jr., Grammer T. C., Brooks J., Glasheen E. M., Wang L. M., Sun X. J., Blenis J., Pierce J. H., White M. F. (1995) The pleckstrin homology domain in insulin receptor substrate-1 sensitizes insulin signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 11715–11718 - PubMed
-
- Myers M. G., Jr., White M. F. (1996) Insulin signal transduction and the IRS proteins. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 36, 615–658 - PubMed
-
- Craparo A., O'Neill T. J., Gustafson T. A. (1995) Non-SH2 domains within insulin receptor substrate-1 and SHC mediate their phosphotyrosine-dependent interaction with the NPEY motif of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 15639–15643 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

