Isorhamnetin, A Flavonol Aglycone from Ginkgo biloba L., Induces Neuronal Differentiation of Cultured PC12 Cells: Potentiating the Effect of Nerve Growth Factor
- PMID: 22761636
- PMCID: PMC3385709
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/278273
Isorhamnetin, A Flavonol Aglycone from Ginkgo biloba L., Induces Neuronal Differentiation of Cultured PC12 Cells: Potentiating the Effect of Nerve Growth Factor
Abstract
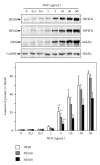
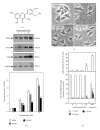
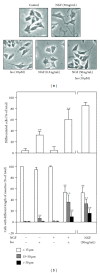
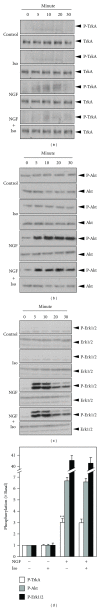
Flavonoids, a group of compounds mainly derived from vegetables and herbal medicines, share a chemical resemblance to estrogen, and indeed some of which have been used as estrogen substitutes. In searching for possible functions of flavonoids, the neuroprotective effect in brain could lead to novel treatment, or prevention, for neurodegenerative diseases. Here, different subclasses of flavonoids were analyzed for its inductive role in neurite outgrowth of cultured PC12 cells. Amongst the tested flavonoids, a flavonol aglycone, isorhamnetin that was isolated mainly from the leaves of Ginkgo biloba L. showed robust induction in the expression of neurofilament, a protein marker for neurite outgrowth, of cultured PC12 cells. Although isorhamnetin by itself did not show significant inductive effect on neurite outgrowth of cultured PC12 cells, the application of isorhamnetin potentiated the nerve growth factor- (NGF-)induced neurite outgrowth. In parallel, the expression of neurofilaments was markedly increased in the cotreatment of NGF and isorhamnetin in the cultures. The identification of these neurite-promoting flavonoids could be very useful in finding potential drugs, or food supplements, for treating various neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease and depression.
Figures



References
-
- Miksicek RJ. Commonly occurring plant flavonoids have estrogenic activity. Molecular Pharmacology. 1993;44(1):37–43. - PubMed
-
- Murkies AL, Wilcox G, Davis SR. Phytoestrogens. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1998;83(2):297–303. - PubMed
-
- Zhu JTT, Choi RCY, Chu GKY, et al. Flavonoids possess neuroprotective effects on cultured pheochromocytoma PC12 cells: a comparison of different flavonoids in activating estrogenic effect and in preventing β-amyloid-induced cell death. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2007;55(6):2438–2445. - PubMed
-
- Choi RCY, Zhu JTT, Leung KW, et al. A flavonol glycoside, isolated from roots of panax notoginseng, reduces amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity in cultured neurons: signaling transduction and drug development for Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2010;19(3):795–811. - PubMed
-
- Zhu JTT, Choi RCY, Xie HQ, et al. Hibifolin, a flavonol glycoside, prevents β-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in cultured cortical neurons. Neuroscience Letters. 2009;461(2):172–176. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

