ZEB2 mediates multiple pathways regulating cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis in glioma
- PMID: 22761708
- PMCID: PMC3383704
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038842
ZEB2 mediates multiple pathways regulating cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis in glioma
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: ZEB2 Mediates Multiple Pathways Regulating Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Apoptosis in Glioma.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 1;15(4):e0231386. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231386. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32236135 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The aim of the present study was to analyze the expression of Zinc finger E-box Binding homeobox 2 (ZEB2) in glioma and to explore the molecular mechanisms of ZEB2 that regulate cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis.
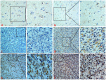
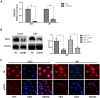
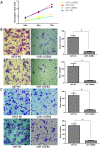
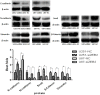
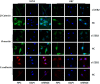
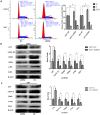
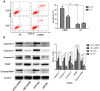
Methodology/principal findings: Expression of ZEB2 in 90 clinicopathologically characterized glioma patients was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. Furthermore, siRNA targeting ZEB2 was transfected into U251 and U87 glioma cell lines in vitro and proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis were examined separately by MTT assay, Transwell chamber assay, flow cytometry, and western blot.
Results: The expression level of ZEB2 protein was significantly increased in glioma tissues compared to normal brain tissues (P<0.001). In addition, high levels of ZEB2 protein were positively correlated with pathology grade classification (P = 0.024) of glioma patients. Knockdown of ZEB2 by siRNA suppressed cell proliferation, migration and invasion, as well as induced cell apoptosis in glioma cells. Furthermore, ZEB2 downregulation was accompanied by decreased expression of CDK4/6, Cyclin D1, Cyclin E, E2F1, and c-myc, while p15 and p21 were upregulated. Lowered expression of ZEB2 enhanced E-cadherin levels but also inhibited β-Catenin, Vimentin, N-cadherin, and Snail expression. Several apoptosis-related regulators such as Caspase-3, Caspase-6, Caspase-9, and Cleaved-PARP were activated while PARP was inhibited after ZEB2 siRNA treatment.
Conclusion: Overexpression of ZEB2 is an unfavorable factor that may facilitate glioma progression. Knockdown ZEB2 expression by siRNA suppressed cell proliferation, migration, invasion and promoted cell apoptosis in glioma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-200b inhibits the growth and metastasis of glioma cells via targeting ZEB2.Int J Oncol. 2016 Feb;48(2):541-50. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3267. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Int J Oncol. 2016. Retraction in: Int J Oncol. 2021 Sep;59(3):65. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5245. PMID: 26648487 Retracted.
-
[Effects of FPR2 gene silencing on the proliferation, migration and invasion of human glioma U87 cells].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018 Sep 23;40(9):659-666. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2018.09.004. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30293389 Chinese.
-
ZEB2-Sp1 cooperation induces invasion by upregulating cadherin-11 and integrin α5 expression.Carcinogenesis. 2014 Feb;35(2):302-14. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt340. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Carcinogenesis. 2014. PMID: 24130169
-
MicroRNA-383 expression regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis in human glioma cells.Tumour Biol. 2015 Sep;36(10):7743-53. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3378-2. Epub 2015 May 4. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25936342
-
Metastasis tumor-associated protein-2 knockdown suppresses the proliferation and invasion of human glioma cells in vitro and in vivo.J Neurooncol. 2014 Nov;120(2):273-81. doi: 10.1007/s11060-014-1558-3. Epub 2014 Jul 22. J Neurooncol. 2014. PMID: 25048531
Cited by
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma progression.Oncol Lett. 2016 Mar;11(3):1615-1620. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4113. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26998052 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing ZEB2 Induces Apoptosis and Reduces Viability in Glioblastoma Cell Lines.Molecules. 2021 Feb 9;26(4):901. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040901. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33572092 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic ZEB2/miR-637/HMGA1 signaling axis targeting vimentin promotes the malignant phenotype of glioma.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Jan 5;23:769-782. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.12.029. eCollection 2021 Mar 5. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 33614228 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased miRNA-637 is an unfavorable prognosis marker and promotes glioma cell growth, migration and invasion via direct targeting Akt1.Oncogene. 2015 Sep 17;34(38):4952-63. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.419. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25597410
-
The investigation of transcriptional repression mediated by ZEB2 in canine invasive micropapillary carcinoma in mammary gland.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 15;14(1):e0209497. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209497. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30645591 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, van den Bent MJ, Mason WP, Weller M, et al. Changing paradigms–an update on the multidisciplinary management of malignant glioma. Oncologist. 2006;11:165–180. - PubMed
-
- Reifenberger G, Hentschel B, Felsberg J, Schackert G, Simon M, et al. Predictive impact of MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma of the elderly. Int J Cancer. 2011. - PubMed
-
- Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007;21:2683–2710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

