Thaliporphine preserves cardiac function of endotoxemic rabbits by both directly and indirectly attenuating NFκB signaling pathway
- PMID: 22761733
- PMCID: PMC3382609
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039174
Thaliporphine preserves cardiac function of endotoxemic rabbits by both directly and indirectly attenuating NFκB signaling pathway
Abstract
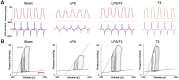
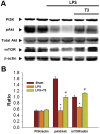
Cardiac depression in sepsis is associated with the increased morbidity and mortality. Although myofilaments damage, autonomic dysfunction, and apoptosis play roles in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction, the underlying mechanism is not clear. All of these possible factors are related to NFκB signaling, which plays the main role in sepsis signaling. Thaliporphine was determined to possess anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective activity by suppressing NFκB signaling in rodents. The purpose of this study is to further prove this protective effect in larger septic animals, and try to find the underlying mechanisms. The systolic and diastolic functions were evaluated in vivo by pressure-volume analysis at different preloads. Both preload-dependent and -independent hemodynamic parameters were performed. Inflammatory factors of whole blood and serum samples were analyzed. Several sepsis-related signaling pathways were also determined at protein level. Changes detected by conductance catheter showed Thaliporphine could recover impaired left ventricular systolic function after 4 hours LPS injection. It could also reverse the LPS induced steeper EDPVR and gentler ESPVR, thus improve Ees, Ea, and PRSW. Thaliporphine may exert this protective effect by decreasing TNFα and caspase3 dependent cell apoptosis, which was consistent with the decreased serum cTnI and LDH concentration. Thaliporphine could protect sepsis-associated myocardial dysfunction in both preload-dependent and -independent ways. It may exert these protective effects by both increase of "good"-PI3K/Akt/mTOR and decrease of "bad"-p38/NFκB pathways, which followed by diminishing TNFα and caspase3 dependent cell apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Annane D, Bellissant E, Cavaillon JM. Septic shock. Lancet. 2005;365:63–78. - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:138–150. - PubMed
-
- Poelaert J, Declerck C, Vogelaers D, Colardyn F, Visser CA. Left ventricular systolic and diastolic function in septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 1997;23:553–560. - PubMed
-
- Munt B, Jue J, Gin K, Fenwick J, Tweeddale M. Diastolic filling in human severe sepsis: an echocardiographic study. Crit Care Med. 1998;26:1829–1833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

