Effects of activin and TGFβ on p21 in colon cancer
- PMID: 22761777
- PMCID: PMC3383701
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039381
Effects of activin and TGFβ on p21 in colon cancer
Abstract
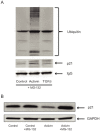
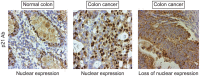
Activin and TGFβ share SMAD signaling and colon cancers can inactivate either pathway alone or simultaneously. The differential effects of activin and TGFβ signaling in colon cancer have not been previously dissected. A key downstream target of TGFβ signaling is the cdk2 inhibitor p21 (p21(cip1/waf1)). Here, we evaluate activin-specific effects on p21 regulation and resulting functions. We find that TGFβ is a more potent inducer of growth suppression, while activin is a more potent inducer of apoptosis. Further, growth suppression and apoptosis by both ligands are dependent on SMAD4. However, activin downregulates p21 protein in a SMAD4-independent fashion in conjunction with increased ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation to enhance migration, while TGFβ upregulates p21 in a SMAD4-dependent fashion to affect growth arrest. Activin-induced growth suppression and cell death are dependent on p21, while activin-induced migration is counteracted by p21. Further, primary colon cancers show differential p21 expression consistent with their ACVR2/TGFBR2 receptor status. In summary, we report p21 as a differentially affected activin/TGFβ target and mediator of ligand-specific functions in colon cancer, which may be exploited for future risk stratification and therapeutic intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
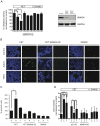
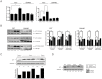
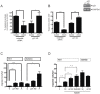
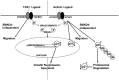
Similar articles
-
Activin and TGFβ use diverging mitogenic signaling in advanced colon cancer.Mol Cancer. 2015 Oct 24;14:182. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0456-4. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26497569 Free PMC article.
-
Activin type 2 receptor restoration in MSI-H colon cancer suppresses growth and enhances migration with activin.Gastroenterology. 2007 Feb;132(2):633-44. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.11.018. Epub 2006 Nov 16. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17258738 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling Activins and Follistatin in Colorectal Cancer According to Clinical Stage, Tumour Sidedness and Smad4 Status.Pathol Oncol Res. 2021 Nov 15;27:1610032. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.1610032. eCollection 2021. Pathol Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34867090 Free PMC article.
-
[TGFbeta, activin and SMAD signalling in thyroid cancer].Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2007 Jul;51(5):683-9. doi: 10.1590/s0004-27302007000500005. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2007. PMID: 17891231 Review. Portuguese.
-
The transcriptional role of Smads and FAST (FoxH1) in TGFbeta and activin signalling.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001 Jun 30;180(1-2):3-11. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00524-x. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11451566 Review.
Cited by
-
Together and apart: inhibition of DNA synthesis by connexin-43 and its relationship to transforming growth factor β.Front Pharmacol. 2013 Jul 19;4:90. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00090. eCollection 2013. Front Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23882217 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeine and its main targets of colorectal cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2020 Feb 15;12(2):149-172. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i2.149. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32104547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sox2-dependent inhibition of p21 is associated with poor prognosis of endometrial cancer.Cancer Sci. 2017 Apr;108(4):632-640. doi: 10.1111/cas.13196. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28188685 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Roles of the Activin Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 14;9(7):821. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070821. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34356885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inactivation of TGF-β signaling and loss of PTEN cooperate to induce colon cancer in vivo.Oncogene. 2014 Mar 20;33(12):1538-47. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.102. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23604118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen YG, Lui HM, Lin SL, Lee JM, Ying SY. Regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis by activin. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2002;227:75–87. - PubMed
-
- Lee YJ, Hong KH, Yun J, Oh SP. Generation of activin receptor type IIB isoform-specific hypomorphic alleles. Genesis. 2006;44:487–494. - PubMed
-
- Mori Y, Yin J, Rashid A, Leggett BA, Young J, et al. Instabilotyping: comprehensive identification of frameshift mutations caused by coding region microsatellite instability. Cancer Res. 2001;61:6046–6049. - PubMed
-
- Hempen PM, Zhang L, Bansal RK, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Murphy KM, et al. Evidence of selection for clones having genetic inactivation of the activin A type II receptor (ACVR2) gene in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Res. 2003;63:994–999. - PubMed
-
- Deacu E, Mori Y, Sato F, Yin J, Olaru A, et al. Activin type II receptor restoration in ACVR2-deficient colon cancer cells induces transforming growth factor-beta response pathway genes. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7690–7696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

